In the fast-evolving landscape of financial services, Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Know Your Customer (KYC), and compliance practices continue to play pivotal roles in safeguarding against financial crimes and ensuring regulatory adherence. As we step into 2024, these cornerstones of financial integrity have undergone significant transformations, spurred by technological advancements, regulatory updates, and emerging global challenges. Understanding the nuances of AML, KYC, and compliance, as well as discerning the latest trends and best practices, is indispensable for financial institutions aiming to navigate this complex terrain effectively. In this blog, we delve into the differences between AML, KYC, and compliance in 2024, while also exploring the most effective strategies and practices to stay ahead in this dynamic regulatory environment.
Imagine your money as a spaceship navigating through the universe of finances. Ever wondered how it stays safe from invisible threats? Well, buckle up as we embark on a financial journey where AML, KYC, and Compliance act like cosmic guardians, keeping your money spaceship secure. Ready for the adventure?
Understanding AML, KYC, and Compliance
Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
AML involves measures and regulations aimed at preventing criminals from disguising illegally obtained funds as legitimate income. Suppose a criminal organization earns money through illegal activities such as drug trafficking. AML measures would include banks and financial institutions implementing procedures to detect and report suspicious transactions, preventing the integration of illicit funds into the legitimate financial system.
Stages of the AML Process
Identification and Verification:
- Verify the identity of customers through reliable documents.
- Use technology like biometrics for enhanced verification.
Risk Assessment and Due Diligence:
- Evaluate the risk linked to each customer.
- Conduct due diligence checks based on the identified risk level.
Monitoring and Reporting:
- Monitor customer transactions for suspicious activities.
- Report and investigate any identified suspicious transactions promptly.
Know Your Customer (KYC)
KYC is a process businesses use to verify and understand the identity of their customers, reducing the risk of fraud and illicit activities.
Example: When someone opens a new bank account, the bank will ask for identification documents, proof of address, and possibly information about the source of income. This KYC process helps the bank ensure that the customer is a legitimate individual and not using the account for illegal purposes.
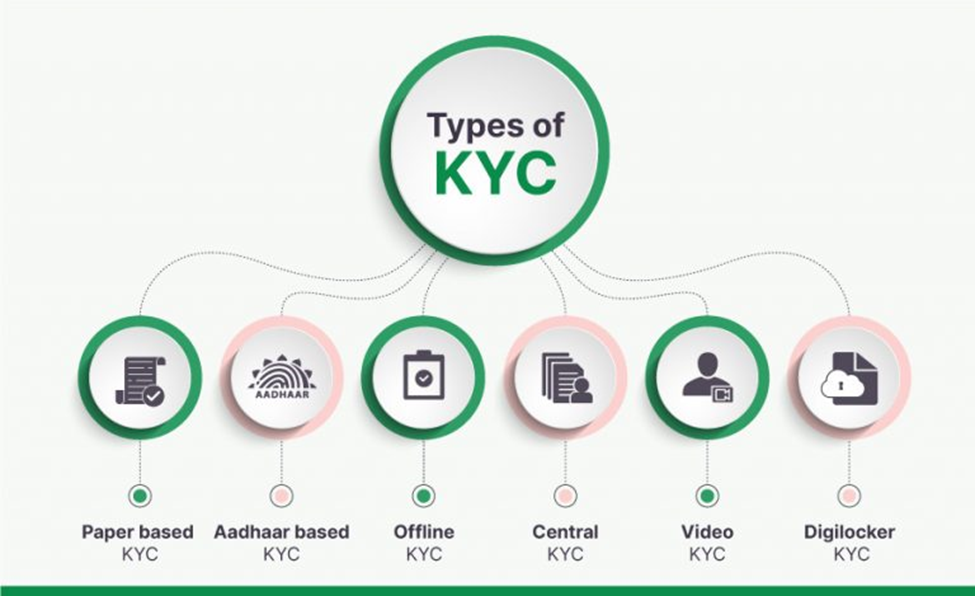
Stages of the KYC Process
Customer Identification:
- Collect and verify customer identity through reliable documents.
- Utilize technology, such as biometrics, for advanced identification.
Risk Assessment and Profiling:
- Assess the risk associated with each customer based on provided information.
- Create risk profiles to determine the level of scrutiny required.
Ongoing Monitoring:
- Continuously monitor customer transactions and activities.
- Update customer profiles and conduct periodic reviews for changes in risk.
Compliance
Compliance involves adhering to rules, regulations, and laws established by governing bodies to ensure ethical and legal business operations.
Stages of the Compliance Process
Regulatory Understanding:
- Attain a thorough grasp of applicable regulations.
- Identify applicable regulatory frameworks for the industry and jurisdiction.
Policy Development:
- Establish robust policies and procedures for compliance.
- Define specific requirements for activities like customer onboarding, due diligence, and reporting.
Implementation and Monitoring:
- Implement compliance measures across the organization.
- Monitor adherence to policies, conduct regular audits, and adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes.
Example: Imagine a financial institution is required by law to report large transactions to the government to combat money laundering. Compliance in this context would involve the institution consistently following this rule, reporting transactions that meet the specified criteria to maintain transparency and adhere to legal requirements.
Evolution of AML, KYC, and Compliance
Historical context of AML, KYC, and Compliance
- AML Origins: Emerging from concerns about illegal funds getting into financial systems.
- KYC Development: Growing due to the increasing complexity of worldwide financial transactions.
- Compliance Foundation: Rooted in legal frameworks, adjusting to societal changes over time.
Milestones and regulatory changes over the years:
| Legislation/Initiative | Year | Significance |
| Bank Secrecy Act (1970) | 1970 | Introduced global record-keeping for AML. |
| Basel Committee (1989) | 1989 | Brought in global AML principles. |
| USA PATRIOT Act (2001) | 2001 | Strengthened AML globally and expanded KYC requirements. |
| EU Money Laundering Directive (2005) | 2005 | Reinforced AML regulations in the EU and introduced risk-based KYC. |
| FATCA (2012) | 2012 | Tackled global tax evasion, impacting KYC practices. |
| GDPR (2018) | 2018 | A landmark in data protection, influencing Compliance practices in KYC. |
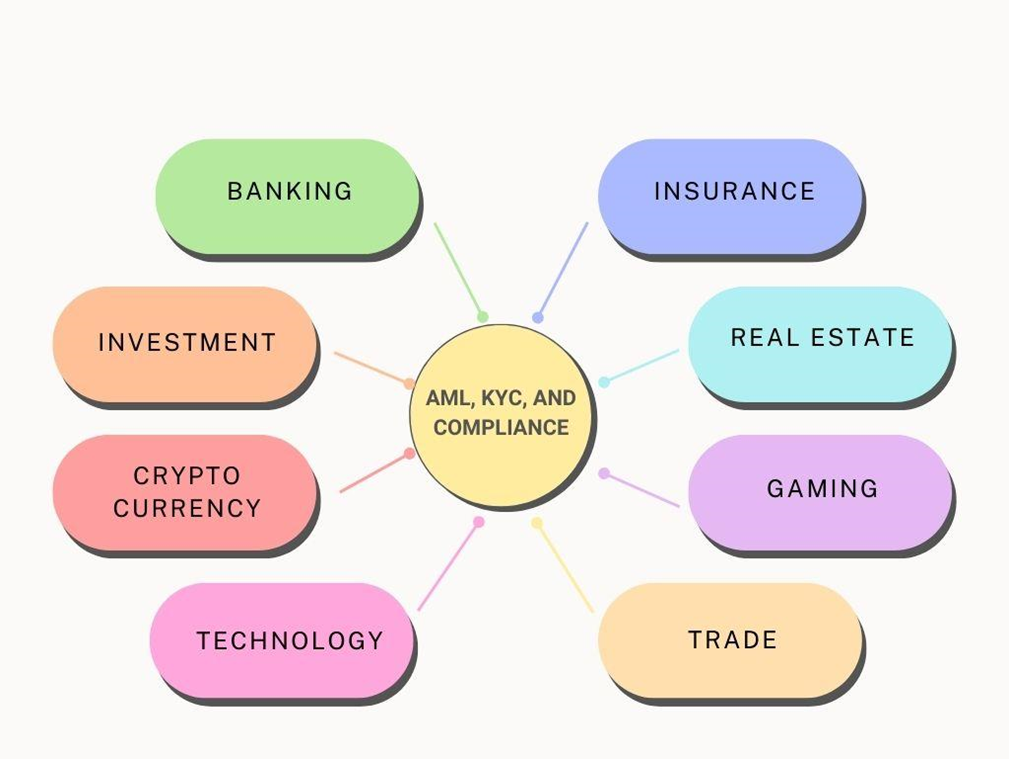
Industries implementing AML, KYC, and Compliance practices
Current Landscape of AML, KYC, and Compliance in 2024
Overview of AML, KYC, and Compliance in 2024
- AML (Anti-Money Laundering): Remains foundational for detecting and preventing illicit financial activities. Stringent regulations and advanced monitoring systems enhance safeguards.
- KYC (Know Your Customer): Evolving with increased reliance on digital identity verification tools. Technology integration enhances accuracy and efficiency in customer identity checks.
- Compliance: Expanding to cover a broader spectrum of regulations. Businesses adopt comprehensive strategies to meet AML, KYC, and various global industry-specific regulations.
Adapting to the Regulatory Landscape: AML and KYC Trends in 2024
Evolving Regulations:
- Ongoing evolution of AML/KYC and beneficial ownership regulations, particularly in the EU.
- Continuous efforts required for compliance in response to dynamic regulatory changes.
Harmonization Challenges:
- CTA (Cryptocurrency Transaction Analysis) and 6AMLD (Sixth Anti-Money Laundering Directive) updates aim for harmonization but present challenges in cross-border compliance.
- Financial institutions grappling with complexities to align with new regulatory frameworks.
Cryptocurrency Scrutiny:
- Cryptocurrencies facing increased scrutiny for alignment with AML, counter-terrorism financing, and sanctions rules.
- Regulators focusing on bringing cryptocurrency activities in line with established financial compliance norms.
Automation for BOI Accuracy:
- Challenges in obtaining accurate Beneficial Ownership Information (BOI) across jurisdictions.
- Growing importance of automation in financial institutions for efficient and accurate BOI processes.
Resource Management and Tech Upgrades:
- Adequate resourcing and budgeting are critical for technology upgrades.
- Financial institutions preparing for increased workloads resulting from a surge in suspicious activity reports.
Impact Assessment and Strategic Response:
- Financial institutions conducting assessments of new regulations’ impacts on compliance processes, data requirements, and staffing.
- Strategic planning to navigate changes effectively in response to evolving regulatory shifts.
Click here to know more: AML KYC – Compliance Trends and Regulations 2024
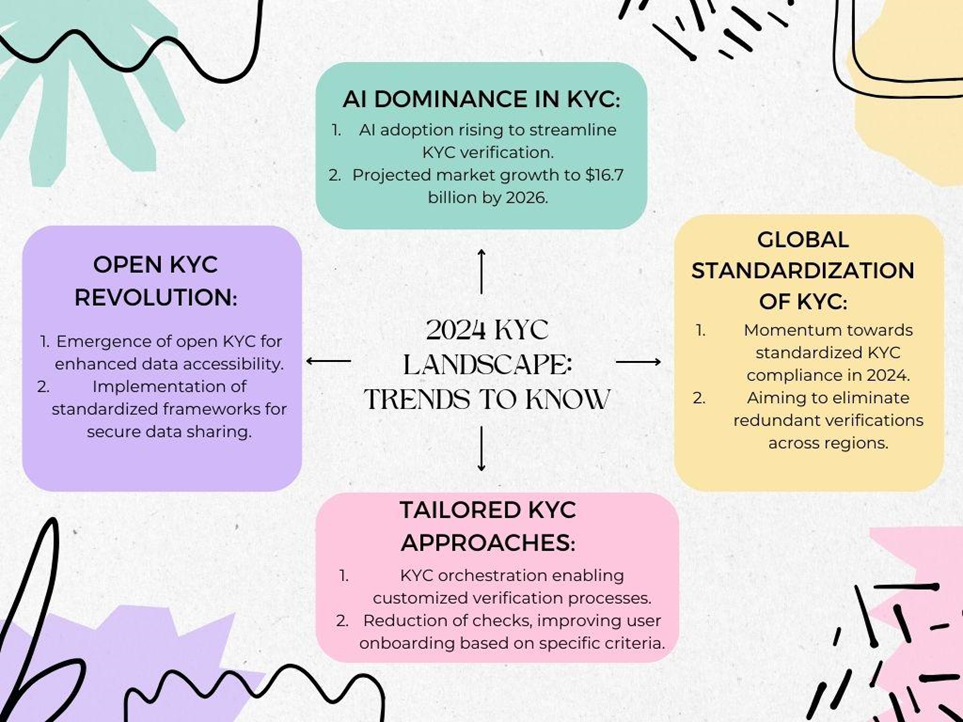
2024 KYC Landscape: Trends to Know
Notable Changes or Advancements in Technology Impacting Practices
| Technology Impacting Practices | Description |
| Blockchain in AML | Blockchain technology is gaining prominence in AML efforts, providing a transparent and immutable ledger for financial transactions. This enhances traceability and helps in detecting suspicious activities. |
| AI and Machine Learning in KYC | Advanced analytics powered by AI and machine learning are revolutionizing KYC processes. These technologies enable quicker and more accurate customer identity verification, reducing the risk of fraudulent activities. |
| RegTech Solutions | The rise of Regulatory Technology (RegTech) solutions is streamlining compliance processes. Automated tools and platforms help businesses stay compliant by efficiently managing regulatory requirements, reporting, and audits. |
Transformation Overview of AML/KYC Landscape in 2024
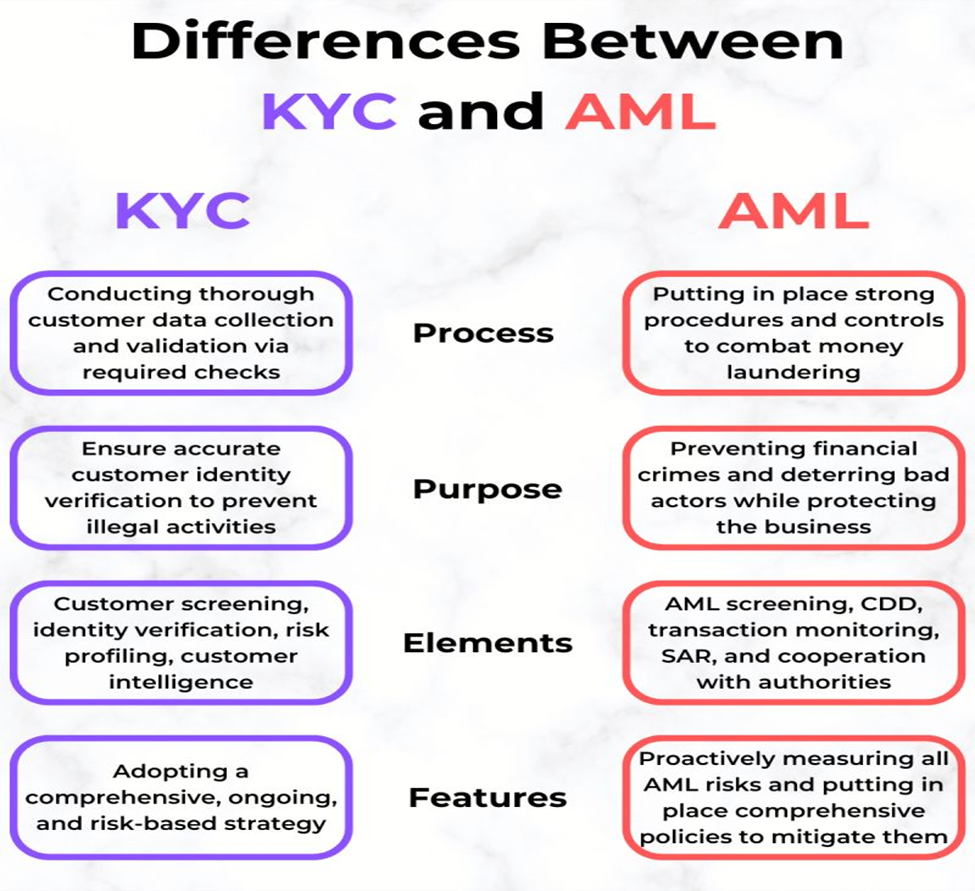
Key Differences of AML and KYC in 2024
Click here to know more about the Key Differences of AML and KYC
Significant Changes in AML and KYC Regulations
- Overview: Significant changes in AML and KYC regulations mirror global advancements and evolving dynamics.
- Technological Integration: Regulations embrace advanced technologies for enhanced efficiency and accuracy in compliance.
- Global Standards: Initiatives to standardize AML and KYC practices globally aim to reduce redundancies for cross-border businesses.
Influence of Technology Advancements
- Technological Integration: Regulations integrate technological solutions to streamline AML and KYC processes efficiently.
- AI and Machine Learning Impact: AI implementation enhances risk assessment and fraud detection capabilities within compliance frameworks.
- Automation for Efficiency: Automated processes are employed to enhance the efficiency of AML and KYC procedures.
New Requirements or Expectations for Businesses in 2024
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD): Businesses are now encountering heightened requirements for due diligence, demanding a more comprehensive examination of customer backgrounds, transactions, and potential risks.
- Real-Time Monitoring: There is an increasing emphasis on monitoring financial transactions in real-time, enabling businesses to promptly identify and address any suspicious activities. This shift enhances the effectiveness of fraud detection and prevention.
- Adaptive Compliance Strategies: Businesses are expected to embrace adaptive compliance strategies capable of evolving in response to the dynamic nature of financial crimes and regulatory changes. This proactive approach ensures ongoing effectiveness in preventing illicit financial activities.
Strategies for Successful Compliance in 2024
The optimal strategies for businesses to maintain and excel in compliance with the latest regulations.
Best Practices for Compliance Excellence
Proactive Risk Assessment:
- Regularly assess and identify potential risks and vulnerabilities.
- Implement preventive measures to mitigate identified risks.
Robust Policies and Procedures:
- Establish clear, comprehensive, and up-to-date compliance policies.
- Ensure policies align with current regulatory requirements.
Employee Training:
- Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees on compliance protocols.
- Keep the workforce informed about the latest regulatory updates.
Continuous Monitoring:
- Implement systems for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of compliance activities.
- Utilize technology to automate monitoring processes and enhance accuracy.
Become Certified AML-KYC Compliance Officer
Importance of a Robust Compliance Framework
- Emphasize the significance of a well-structured compliance framework.
- Discuss the role of technology in enhancing compliance efforts, such as automated monitoring and reporting systems.
Technology’s Role in AML and KYC
Impact:
- Enhances AML and KYC processes, ensuring operational efficiency.
- Enables real-time identification of suspicious activities.
- Facilitates synchronized global compliance efforts.
Advanced Technologies:
- Utilizes AI for precise identification of money laundering patterns.
- Adapts ML to evolving patterns, enhancing risk assessments.
- Streamlines tasks through automation, reducing errors.
Challenges and Risks:
- Elicits concerns about data privacy, requiring robust measures.
- Addresses algorithmic bias through regular auditing.
- Manages integration challenges for seamless technology adoption.
Why AML, KYC, and Compliance are Important
Critical Role in Preventing Financial Crimes
AML (Anti-Money Laundering):
- Identification and Prevention: AML processes are crucial in identifying and preventing the integration of illegally obtained funds into the financial system.
- Safeguarding Financial Institutions: AML measures safeguard financial institutions from unwittingly facilitating money laundering activities.
KYC (Know Your Customer):
- Identity Verification: KYC practices play a pivotal role in verifying customer identities, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraudulent activities.
- Transaction Authorization: Knowing the customer allows businesses to authorize transactions with confidence, preventing unauthorized and potentially illicit activities.
Compliance:
- Ethical Business Operation: Compliance ensures businesses operate ethically, transparently, and in adherence to regulations.
- Risk Mitigation: Compliance practices mitigate risks, identify potential illegal activities, and contribute to the overall integrity of the financial system.
Real-World Examples
HSBC Money Laundering Scandal (2012):
- Importance of AML: HSBC faced severe consequences for facilitating money laundering, emphasizing the critical role of robust AML measures in preventing such scandals.
Equifax Data Breach (2017):
- Importance of KYC: The Equifax breach highlighted the need for strong KYC practices to protect customer identities and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Wells Fargo Account Fraud (2016):
- Importance of Compliance: Wells Fargo’s account fraud scandal underscored the significance of compliance in maintaining ethical business practices and avoiding fraudulent activities.
Impactful AML, KYC, and Compliance Case Studies
Against tax evasion strategies and techniques exist to assist monetary foundations with combating illegal tax avoidance by keeping lawbreakers from participating in exchanges that are painstakingly masked which are associated with criminal operations.
Even though it’s easy for us to keep stressing how important KYC and AML processes are, you might not realize how much it could cost your business if they are done wrong or ignored. This is not just because you could lose money and your reputation, but also because you could face official sanctions and punishment if you break KYC and AML requirements in regulated industries like finance.
To comprehend that it is so vital to guarantee your KYC and AML strategies are exceptional, we should take a gander at a couple of cases lately, and their results.
Falcon Private Bank:
One of the most notorious cases in the industry to date, Falcon Private Bank faced severe penalties, including the withdrawal of its merchant bank status and a fine of S$4.3 million. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) cited serious failures in their AML controls and improper conduct by senior management, allowing the bank to be used in Malaysia’s 1MDB embezzlement scandal.
Bank J Safra Sarasin:
In April 2021, MAS imposed a composition penalty of S$1 million on Bank J Safra Sarasin for significant breaches of AML requirements between March 2014 and September 2018. The bank’s lapses in AML control procedures during customer onboarding and ongoing monitoring increased the risk of being used for illegal activities.
Role of AML, KYC, and Compliance in preventing financial crimes
| Aspect | AML (Anti-Money Laundering) | KYC (Know Your Customer) | Compliance |
| Role | Identifies and prevents the integration of illegally obtained funds into the financial system. | Verifies customer identities, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraudulent activities. | Ensures businesses operate ethically, transparently, and in adherence to regulations. |
| Impact | Safeguards financial institutions from unwittingly facilitating money laundering activities. | Prevents unauthorized transactions and ensures a thorough understanding of customer behavior. | Mitigates risks, identifies potential illegal activities, and contributes to the integrity of the financial system. |
2024 Vision: Transformations in Practice
Navigating the Future
Dynamic Landscape: The AML, KYC, and Compliance landscape is ever-evolving, requiring constant vigilance and adaptation to stay ahead.
Technological Integration: Advancements in technology, including AI and automation, play a pivotal role in enhancing the effectiveness of AML, KYC, and Compliance processes.
Adaptive Compliance: Businesses must adopt adaptive compliance strategies, emphasizing real-time monitoring, proactive risk assessment, and continuous training to navigate the complex regulatory environment.
Importance of Adapting to Changes
Adapting to changes is not just a necessity but a strategic imperative. It ensures businesses remain resilient, compliant, and capable of mitigating emerging risks in the financial sector. Continuous evolution in strategies and technologies is essential to stay ahead of financial crimes and maintain trust.
Providing Resources
For those seeking further information or staying updated on AML, KYC, and Compliance:
- Regulatory Authorities: Regularly check updates from financial regulatory authorities for the latest guidelines.
- Industry Publications: Explore industry publications and journals covering financial regulations, providing in-depth insights and analyses.
- Professional Networks: Join professional networks and forums to engage with experts, discuss emerging trends, and share best practices.
- Training Programs: Enroll in specialized training programs and courses to enhance skills and stay abreast of the latest compliance requirements.
Tools employed for AML, KYC and Compliance purposes
Various tools play a crucial role in Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Know Your Customer (KYC), and Compliance efforts:
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Tools:
- Verify and understand customers’ backgrounds.
- Identify potential risks and ensure compliance with regulations.
Identity Verification Solutions:
- Use biometrics, document verification, and digital identity checks.
- Authenticate customer identities securely.
Transaction Monitoring Systems:
- Automate tracking and analysis of financial transactions in real-time.
- Detect suspicious activities and prevent money laundering.
Regulatory Reporting Software:
- Streamline the generation and submission of reports required by regulatory authorities.
- Ensure compliance with reporting obligations.
Risk Assessment Software:
- Evaluate the risk associated with customers, transactions, or business relationships.
- Enhance decision-making processes.
Blockchain Analytics:
- Monitor and analyze transactions on blockchain networks.
- Identify illicit activities associated with cryptocurrencies.
AI and ML Tools:
- Enhance KYC processes, risk assessment, and fraud detection.
- Use advanced analytics and pattern recognition.
Cybersecurity Solutions:
- Protect sensitive customer data and ensure the integrity of compliance processes.
- Guard against cyber threats and unauthorized access.
Data Management Systems:
- Effectively manage and secure large volumes of data.
- Ensure accuracy and facilitate seamless compliance processes.
Collaboration Platforms:
- Enable communication and information-sharing among financial institutions, regulators, and technology providers.
- Enhance collective efforts in combating financial crimes.
These tools collectively contribute to a robust framework for financial institutions, regulators, and businesses to navigate the complexities of AML, KYC, and Compliance.
Learn more about tools here: Click here
Tools dedicated to specific functions within KYC, AML, and Compliance domains, providing organizations with tailored solutions for their regulatory needs.
| KYC Tools | AML Tools | Compliance Tools |
| SEON | SEON | Sprinto |
| Onfido | ComplyAdvantage | Connecteam |
| Trulioo | Acuris Risk Intelligence | SiteDocs |
| Refinitiv | OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control) | Qualtrax |
| KYC-Chain | SumSub | PowerDMS |
| Token of Trust | Token of Trust | QT9 |
In 2024, AML, KYC, and compliance demand a proactive stance. Understanding regulatory nuances, implementing best practices, and embracing advanced technologies are crucial. Non-compliance risks regulatory actions, emphasizing the need for robust frameworks. Continuous monitoring, adaptive strategies, and ongoing training are key for success. A holistic approach fosters resilience and integrity in the evolving financial landscape.
AML KYC Complaince Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Why are AML and KYC crucial in 2024?
- A: AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer) play a vital role in ensuring financial integrity. They thwart illicit financial activities, enhance transparency, and align with evolving regulatory standards.
Q2: How can businesses navigate evolving AML/KYC regulations?
- A: Businesses can maintain compliance by actively tracking regulatory updates, establishing robust compliance frameworks, and harnessing technology for efficient AML/KYC processes.
Q3: Why is technology integration vital for AML and KYC practices?
- A: Technology enhances precision and efficiency in AML and KYC processes. The incorporation of AI, machine learning, and automation streamlines compliance, providing real-time insights and risk assessments.
Q4: What are the repercussions of AML non-compliance?
- A: Non-compliance carries severe consequences, including hefty fines, legal repercussions, damage to reputation, and missed business opportunities. Maintaining vigilance is imperative.
Q5: How can businesses ensure continuous compliance in a dynamic landscape?
- A: Businesses should conduct regular internal audits, stay abreast of industry best practices, invest in employee training, and adapt AML/KYC processes to evolving threats.
Q6: What role does automation play in AML and KYC procedures?
- A: Automation streamlines AML and KYC procedures, facilitating quick and accurate transaction monitoring, customer due diligence, and compliance reporting, thereby reducing manual errors.
Q7: How do AML and KYC contribute to a secure financial ecosystem?
- A: AML and KYC practices establish a secure financial environment by preventing money laundering, fraud, and illicit activities. They promote trust, transparency, and adherence to regulatory compliance.
Q8: What are the key trends influencing AML compliance in 2024?
- A: Trends encompass heightened regulatory focus, integration of advanced technologies like blockchain and AI, emphasis on continuous monitoring, and the necessity for global collaboration.
Content Author: Jyoti Rawat, an accomplished Digital Marketing and E-commerce Manager with over 9 years of experience. Graduated with a B.Tech in Computer Engineering, together with a passion for curating content that educates, connects, and drives engagement. Committed to delivering quality work, she aims to equip individuals with the knowledge needed to navigate the digital landscape confidently, fostering meaningful interactions and informed decision-making.