First let us see what do we understand by the Term IT?
Information technology means keeping data we have or to use the data that is collected for some business or other enterprise. IT is said to be a subset of information and communications technology.
Growing Importance of IT sector in India
The Indian IT sector has played a great role in contributing to the economic progress of India and the ever expanding socio-economic infrastructure has been a pillar of strength in supporting the growth of Indian information technology industry.
The growing Indian economy has helped the IT sector to maintain a competitive edge in the global market. The IT and its enabled services industry in India have observed a growth rate of 22.4% in the previous year. The total revenue from the IT sector was valued at 2.46 trillion Indian rupees in the year 2007. The local IT market in India has accounted for 900 billion rupees.
Growth of India’s IT industry
The growth of India’s IT industry depends on some critical factors. These are as follows:
- In India there a large number of IT professionals who have the required skill and calibre to meet up to the demands of the Global IT Sector.
- The cost of skilled labour in India is fairly low and as compared to other developed nations. So MNC’s have extended their businesses in India as they are getting high profits due to this.
- India has a huge number of English-speaking IT professionals. This is the reason why the English-speaking countries like the US depend on the Indian IT industry for expanding their businesses.
The emergence of information technology sector in India has brought a lot of changes in the Indian job market. The IT sector of India offers ample opportunities of employment. With IT Giants like Infosys, Cognizant, Wipro, Tata Consultancy Services and other IT firms in major Indian cities, there is no shortage of job opportunities for the Indian IT professionals. The IT enabled sector of India takes a huge number of graduates from general stream within the BPO and KPO firms. So in conclusion we can say that the growth of India’s IT industry has been responsible in initiating the economic progress of India.
Here is the Statistics of IT & BPO in India
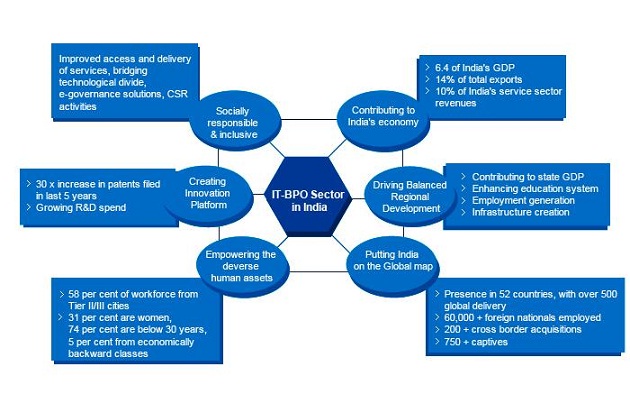
Achievements of IT Sector:
- Increase in international sourcing industry from 51% in 2009 to 58% in 2011.
- Contribution to India’s GDP has increased from 1.2% in 1998 to 7.5% in 2012.
Demand & Supply
Due to the expansion in IT sector in terms of type, volume etc., there is an ever growing demand for engineering graduates, skilled work force etc. Being a service headed industry; this sector is extremely reliable on manpower. While there is enough of supply of graduates, it is very crucial for the labour to be technically competent and possess soft skills.
Now let us look at the challenges faced by Indian IT Sector…

1. Uncertain global economy: The Indian IT business industry gets about 75% of its revenues from USA and Europe. The new concern regarding the European sovereign debt has restricted companies to slow down their IT spending. BFSI segment has always been the largest contributor to Indian IT revenues. As shown within the figure below, the recent turmoil in Europe & US has resulted in slowing demand in BFSI segment.
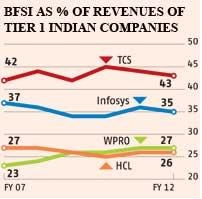
2. Tough Competition from MNC’s: There has been increased competition from MNC’s like IBM to Indian IT firms. This has led to decrease in wages of employees.
3. Low Worker Utilization: Increasing bench size has been reported across numerous IT firms. Employee utilization has fallen down to alarming 67% for a number of Indian companies. Companies have to reserve certain human capital so as to accommodate them just in case of future demand.
4. Pressure on charge rates: Discounts from key financial sector clients is pinching IT corporations. On 12th July, Infosys claimed that valuation has fallen by 3.7% in the June quarter from the previous quarter. As the growth in demand has fallen, firms are opting for price cuts.
Major Players in Indian IT
1. TCS is the largest software company in Asia and was one of the pioneers of the global delivery model. Its Q1 results are slightly higher than expected with 14.6% increase (over previous quarter) in Q1 profit at Rs 3280 crore with revenues at Rs 14869 crores. TCS has mentioned that it is expecting to beat the forecasts of 11-14% growth in revenues set by NASSCOM for FY13.
2. Infosys is the 2nd largest Indian IT service provider and it is known for its work ethics and top notch management practices. In the past the company had exceeded revenue expectations, which kept investors and analysts happy. But by failing to meet expectations in three of the five recent quarters, it has lost its status as the industry bellwether. It has cut down its revenue forecasts for FY13 to five per cent down from its April estimate of ten per cent growth. The corporate has a weak economic environment, not able to meet up to client expectations and fall in discretionary spending as the reason behind its fall in revenues.
3. Wipro is the 3rd biggest Indian IT firm and its revenues for the year 2011-12 stood at $5.7 billion. It is focusing on regions like Latin America, Asia Pacific and Ghana as they are contributing almost 16-17% of the total revenues for Wipro. Wipro is shifting its focus from telecom equipment vendors who have reduced IT spending to telecom analytics and mobile broadband where the end users are telecom operators.
4. HCL Technologies is the 4th largest Indian IT company. In the last two quarters, it has won deals worth $2.5 dollars and Europe has contributed almost 54% to it. It is strong in total IT outsourcing that includes infrastructure services, application development and maintenance.
Let us look at what are the Major IT Hubs in India…
- Bangalore: Banglore is known as the Silicon Valley of India. Most of biggest IT firms are located here. Notable tech parks are Embassy Golf Link, Bagmane Tech Park.
- Chandigarh: It is one of the growing international IT services and outsourcing exporters. Rajiv Gandhi Chandigarh Technology Park and Phase 8b Mohali are important tech park of the city.
- Hyderabad: Hyderabad known for the HITEC City or Cyberabad is a major global technology hub and the largest bioinformatics hub in India. Notable tech parks are HITEC City, Genome Valley.
- Kolkata: Kolkata is also one of the leading Indian and international IT services and outsourcing exporter.
- Pune: It is one of the leading Indian and international IT services and outsourcing exporters. The next biggest IT park of India (Rajiv Gandhi IT Park at Hinjawadi) has been expected to scale up to phase 7.
- Chennai: Chennai has a great IT infrastructure with expressway known as IT expressways, and many other IT parks.
Now we have enough knowledge about what is IT Sector, what are its advantages, drawbacks etc. We also very well know that we have to keep updating our self in the IT field as technology changes every day, new things come into existence.
Now, for people who are interested in working in IT Field, let us look at the:
Top 10 IT Skills in Demand in 2019
- Cloud Computing
- Artificial Intelligence
- Analytical Reasoning
- Machine Learning
- UX Design
- Mobile Application Development
- Social Media Marketing
- Scientific Computing
- Game Development
- Data Science
Now let us go through them one by one.
CLOUD COMPUTING
Cloud Computing is a generic term for anything that involves providing hosted services over the Internet it was introduced as the users needed more space to store things. These are broadly divided into three categories: Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Cloud computing was inspired by the cloud symbol.

A cloud service has three distinct characteristics that make it different from traditional web hosting. It is sold on demand, mainly by the minute or the hour, it is flexible as a user can have as much or as little of a service as they need at any given time, and the service is only managed by the provider.
A cloud may be private or public. A public cloud sells services to anyone who wants its services. Presently, Amazon Web Services is the largest public cloud provider. A private cloud is a network or a data centre that supplies hosted services to a handful number of people. Private or public, the main aim of cloud computing is to provide easy, scalable access to computer resources and IT services.
Cloud Computing Models
Private Cloud services are delivered from a data center to internal users. This model offers the flexibility and convenience of the cloud, whereas protecting the management, control and security common to local data centres. Private cloud technologies include VMware and OpenStack.
In the public cloud model, a third-party cloud service supplier delivers the cloud service over the internet. Public cloud services are sold on demand, usually by the minute or hour, though long-term commitments are available for several services. Customers pay for the CPU cycles, storage or bandwidth they consume. There are many public cloud service providers, but the ones at the top are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, IBM and Google Cloud Platform.
A hybrid cloud is a mixture of public cloud services and an on-premises private cloud, with automation between the two. Corporations will run mission-critical workloads or sensitive applications on the private cloud and use the public cloud to handle workload or spikes in demand. The main aim of a hybrid cloud is to create a unified and automated environment that takes advantage of all that a public cloud can provide, while maintaining the data.
Cloud Computing Characteristics and Benefits:
- Self Service Provisioning: End users can use compute resources for almost any type of workload on demand. This eliminates the need for IT administrators to provide and manage compute resources.
- Elasticity: Corporations can scale up as computing needs increase and scale down again as demands decrease. This eliminates the need for massive investments in the infrastructure.
- Pay per use: Compute resources are measured at a granular level, enabling users to pay only for the resources and workloads they use.
- Workload resilience: Cloud service providers typically implement most occurring resources to keep storage and to keep important workloads of user’s running often across multiple global regions.
- Migration flexibility: Organizations will move certain workloads to or from the cloud or to different cloud platforms as desired for better cost savings or to use new services as they emerge.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
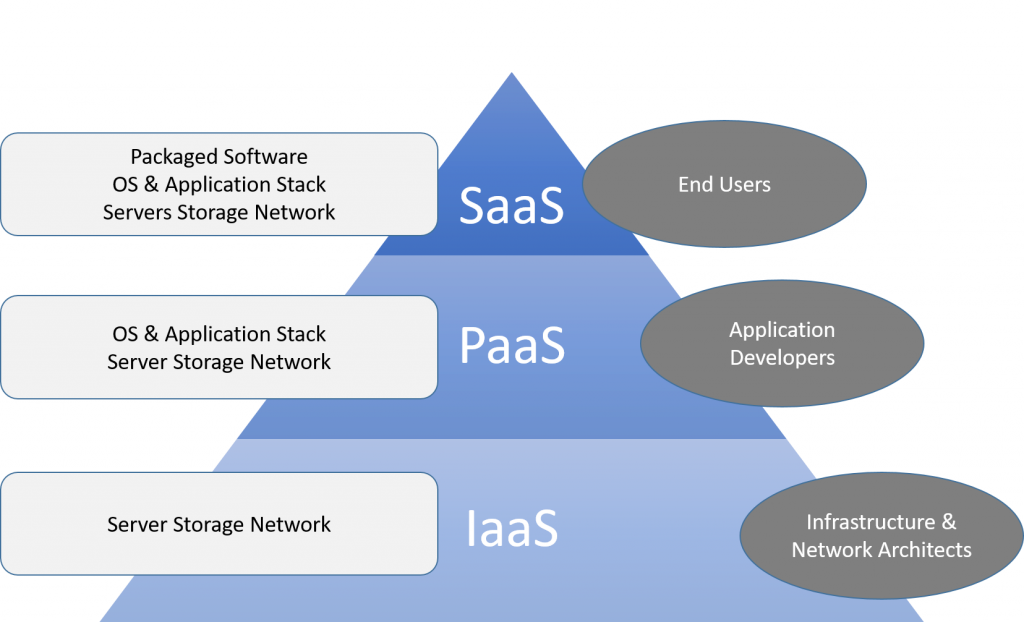
Cloud computing has changed over time, it has been divided into three different service categories: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and software as a service (SaaS).
IaaS providers supply a virtual server instance and storage, and APIs that enable users to migrate workloads to a VM. Users have a fixed storage capacity and can start, stop, access and configure the VM and storage as we desire. IaaS providers offer small, medium, large clouds in addition to customized instances, for various workload needs.
In the PaaS model, cloud suppliers host development tools on their infrastructures. Users access these tools over the internet using web portals or gateway software. PaaS is used for general software development, and many PaaS suppliers host the software after it’s developed. PaaS providers include Salesforce, AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Google App Engine.
SaaS is a distribution model that delivers software applications across the internet; these applications are called web services. Users will access SaaS applications and services from any location using a computer or mobile device that has internet connection. Most common example of a SaaS application is Microsoft Office 365 for productivity and email services.
Let us look at the diagram of the type of services.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
John McCarthy, who named the term in 1956 and defines it as “the science and engineering of making intelligent machines.

Some other names for the field have been proposed, which are computational intelligence, synthetic intelligence or computational rationality.
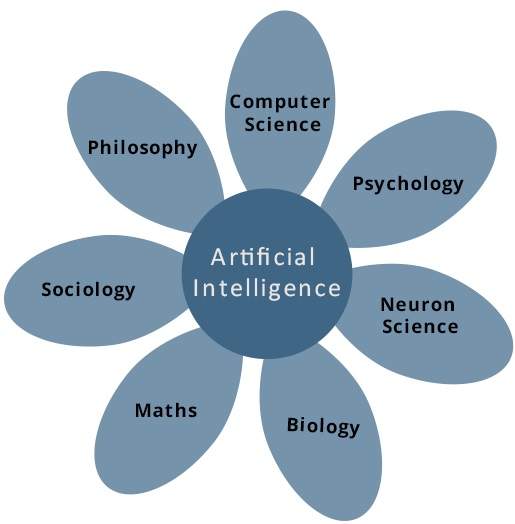
Artificial intelligence is also used to describe a property of machines or programs which is the intelligence that the system demonstrates. Artificial Intelligence research uses tools and information from many fields, including computer science, psychology, philosophy, neuroscience, cognitive science, linguistics, probability, optimization and logic.
Artificial Intelligence analysis also overlaps with tasks such as robotics, control systems, data mining, logistics, speech recognition, facial recognition and many other tasks. Learning of the machine is based on empirical data and is associated with non-symbolic AI, scruffy AI and soft computing.
Goals of AI
- To Create Expert Systems: To develop a systems which can exhibit intelligent behaviour, learn, demonstrate, explain, and advice its users.
- To Implement Human Intelligence in Machines: To create systems that understand, think, learn, and behave just like humans.
Application of AI
- Gaming: AI plays a major role in strategic games such as chess, poker, tic-tac-toe, etc., where machine have to think of a large number of possible positions.
- Natural Language Processing: It has now been made possible to interact with the computer that understands the language spoken by humans.
- Expert Systems: There are some special applications that integrate machine, software, and special data to impart reasoning and advising. They provide explanation and recommendation to the users.
- Vision Systems: These are the systems which understand, observe, interpret, and comprehend visual input on the computer. For example,
- A spying aeroplane takes photographs, which are used to figure out spatial information or map of the areas.
- Nowadays, Doctors using clinical expert system to diagnose the patient.
- Police using computer software that is able to recognize the face of criminal with the stored portrait created by forensic artist.
- Speech Recognition: Some intelligent systems have the capability of hearing and understanding the language in terms of sentences and their meanings while a human talks to it. It will still recognize your voice if you use different accents, slang words, noise in the background, change in human’s noise due to cold, etc.
- Handwriting Recognition: The handwriting recognition software reads the text which is written on paper by a pen or on the screen by a stylus. It is also able to recognize the shapes of the letters and convert it into editable text.
- Intelligent Robots: Robots are made intelligent enough to perform the tasks given by a human. They have sensors located inside them to detect physical data from the real world such as light, heat, temperature, movement, sound, bump, and pressure. They have highly efficient processors, multiple sensors and huge amount of memory, to exhibit intelligence. They are also capable of learning from their mistakes and can easily adapt to the new environment.
COMPUTER GRAPHICS
Computer graphics is the production of images on computers which can be used in any medium. Images that are used in the graphic design are often produced on computers, as well as the still and moving images we see in animations. The real life images seen in electronic games and computer simulations would not have been created or supported without the enhanced capabilities of modern day computer graphics.
Computer graphics are also important for scientific visualization, a part of computer graphics that uses images and colours to model complex phenomena such as air currents and electric fields, in which objects are drawn on computer and analyzed in computer programs. Even the windows-based graphical user interface, which is a common means of interacting with a lot of computer programs, is associated with computer graphics.
Advantages
- It provides us tools for producing pictures of real world objects as well as of abstract, synthetic objects such as mathematical surface in 4D and that of data which have no geometry such as survey results.
- It has the inbuilt ability to show moving pictures and thus make it possible to produce animations with computer graphics.
- With the use of computer graphics user can control the animation speed, the geometric relationship the object in the scene to one another, the amount of detail shown and on.
- The computer graphics provides us with a tool which is called motion dynamics. With this tool the user is able to move and tumble objects with respect to a stationary observer, or if he wants he can make objects stationary and the viewer moving around them.
- The computer graphics has also provided the facility called update dynamics. With this technology we can change the shape, colour or other properties of the objects being viewed.
Disadvantage
- It is not easy to create effective Computer Graphics.
- A lot of resources are involved in CG creation, it make’s cost very high, and it takes more time to create.
MACHINE LEARNING
Machine Learning is mainly based on algorithms and they are a sequence of instructions used to solve a problem. Algorithms are developed by programmers to instruct computers in new tasks and are the building blocks of the advanced digital world which we are seeing today. Computer algorithms can organize a large amount of data into information and services that are based on certain instructions and rules.
Instead of programming the computer every step of the way, this approach offers the computer directions that allow it to learn from data without new instructions at each step by the programmer. This means that computers can be used for new, complicated tasks that were not possible to program manually. Tasks like photo recognition applications for the visually impaired or the task of translating pictures into speech.
The basic process of machine learning is to give the data which is acquired during training to a learning algorithm. The learning algorithm then generates a new set of rules, based on inferences from the data. By using different types of training data, the same learning algorithm can be used to generate different types of models. For e.g. this type of learning algorithm could be used to teach the computer how to translate different languages or predict the stock market.
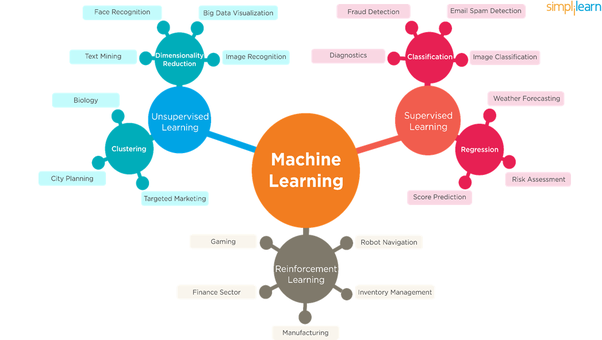
How Machines Learn?
- Supervised learning: The learning algorithm is given a set of data which is labelled and the desired output. For e.g., pictures of dogs labelled “dog” will help the algorithm identify the rules to classify pictures of dogs.
- Unsupervised learning: The data given to the learning algorithm is not labelled, and the algorithm is asked to search for patterns in the input data. For e.g., the recommendation system of an e-commerce website where the learning algorithm discovers similar items often bought together.
- Reinforcement learning: The algorithm interacts with a dynamic environment and keeps learning from experience and provides feedback. For e.g., self-driving cars.
The current growth in Artificial Intelligence and machine learning is tied to developments in three important areas
- Data availability: We can say that over 3 billion people are online with around 17 billion connected devices or sensors, which generate a large amount of data which when combined with decreasing costs of data storage, can be easily available for use. Machine learning can use this as training data for learning algorithms and hence making new rules to perform increasingly complex tasks.
- Computing power: Powerful computers and their ability to connect remote processing power through the Internet and make it possible for machine learning techniques to process these huge amounts of data.
- Algorithmic innovation: These new machine learning techniques, specifically in neural networks which is also known as “deep learning” have inspired new services, but is also making investments and research in other parts of the field.
Challenges
- Decision-making: With artificial intelligence performing tasks ranging from self-driving cars to managing insurance pay-outs, it’s critical we understand decisions made by an AI agent.
- Data Quality and Bias: In ML, the model’s algorithm will only be as good as the data it trains on. This means biased data will result in biased decisions. For example, Legal jurisdictions in the United States are using algorithms that assess the risks to determine an offender’s risk of committing a crime in the future. But, if these algorithms are trained on racially biased data, they may cause greater risk to individuals of a certain race over others.
- Safety and Security: As the Artificial Intelligence agent learns and interacts with its surroundings, there are many challenges related to its safe deployment. They can stem from unpredictable and harmful behaviour, including indifference to the impact of its actions.
- Accountability: The strength and accuracy of learning algorithms is based on their ability to generate rules without instructions at each step. While this technique has proved efficient in accomplishing complex tasks such as face recognition or understanding natural language, it is also a source of concern.
- Governance: The institutions, processes and organizations involved in the governance of Artificial Intelligence are still in the budding stages. We can say Privacy and data laws are its examples.
- Social and Economic Impact: It is predicted that Artificial Intelligence technologies will bring economic changes which will result in increase in productivity. This includes the use of machines which will be able to perform new tasks, such as self-driving cars, advanced robots or smart assistants to support people in their daily lives.
UX DESIGN
User experience (UX) design is the process of creating products that provides us with meaningful and relevant experiences to the users. This involves the design of the entire process of acquiring the product and including aspects of branding, design, usability, and function.
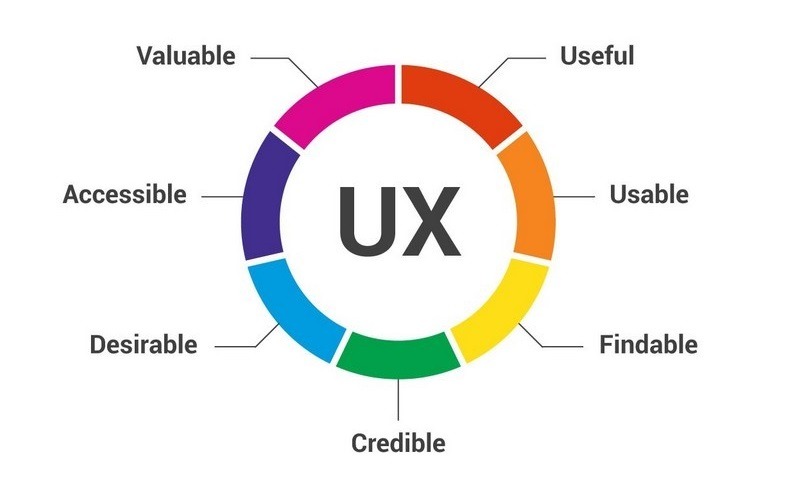
User Experience Design is usually associated with terms like User Interface Design and Usability, Usability and User Interface Design are important aspects of UX Design. A UX designer is concerned with the entire process of acquiring and integrating a product which includes aspects of branding, design, usability and function.
UX designers don’t just focus on creating products that are usable; they concentrate on other aspects of the user experience, such as pleasure, efficiency and fun, too.
UX-Design is User Centered
Since UX design takes note of the entire user journey, it’s a multidisciplinary field. UX designers come from a variety of backgrounds such as visual design, programming, and psychology and interaction design.
A UX designer’s typical tasks vary, but often include user research, creating personas, designing wireframes and interactive prototypes as well as testing designs.
These tasks can vary greatly from one corporation to the next, but there is always a demand for designers to be the users’ advocate and keep the users’ needs at the center of all design and development efforts.
MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT
Mobile application development is the process by which a mobile application is developed for mobile devices.
The difference between a good application and a bad application is usually because of the quality of its user experience (UX). A good UX design is what separates successful apps from unsuccessful ones. Nowadays, mobile users expect a lot from an application such as fast loading time, ease of use and delight during interaction. If you want your application to be successful, you have to consider UX to be not just a small aspect of design, but an essential part of product strategy.
What to work on in Mobile Development?
- Minimize Cognitive Load: Cognitive load here refers to the amount of brain power required to use the application. The human brain has a limited amount of processing power, so you should keep in mind to not provide too much information at once, it might overwhelm the user and make them abandon the task.
- Decluttering: Clutter is one of the worst enemies of good design. By cluttering your interface, you overload users with a lot of information: Every added button, image and icon makes the screen more complicated, so make sure to keep it simple. Clutter is terrible on desktop, but it is more worse on mobile .It’s essential to get rid of anything in a mobile design that is not necessary because reducing clutter will improve comprehension.
- Offload Tasks: Welook for anything in the design that requires user effort, and look for other alternatives. For example, in some cases you can reuse previously entered data instead of asking the user to type again, or use already available information.
- Familiar Screens: Familiar screens are those screens which the users see in many apps. Screens such as “Getting started,” “What’s new” and “Search results” have become standards for mobile applications. They do not require additional explanation because these features are known to the users. This allows users to use prior experience to interact with the application, with no learning curve.
- Anticipate User’s Needs: We look for steps in the user journey where users might need help.
- Avoid Jargon: Clear communication should always be a top most priority in any mobile application. Use what you know about the audience you are targeting to determine whether certain words or phrases are appropriate.
- Make the Design Consistent: Consistency is a fundamental principle of design. Consistency eliminates confusion. Maintaining an overall consistent appearance throughout an application is essential.
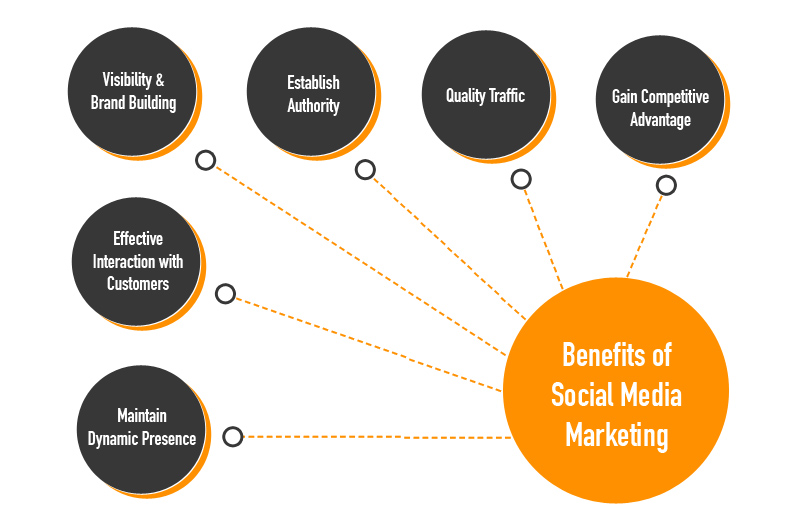
SOCIAL MEDIA MARKETING
Social media marketing is the most powerful way for businesses to reach prospects and customers. The customers are already interacting with brands via social media, and if you do not speak directly to your audience through social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Pinterest, you’re missing out the opportunity to promote your product. Good marketing is the main element of social media marketing and can bring success to your business.

Social media marketing, or SMM, is a type of internet marketing that involves creating and sharing your content on social media in order to achieve the marketing goals set by your corporation. Social media marketing includes activities like posting text and uploading images or videos, and other content that keeps the audience engaged, as well as paid social media advertising.
Social Media Marketing can help meet a number of goals, such as:
- SMM can help in increasing the website traffic
- SMM can help in building conversions
- Raising brand awareness of a product
- To create a brand identity and positive brand association
- Improving communication and interaction with the key audiences
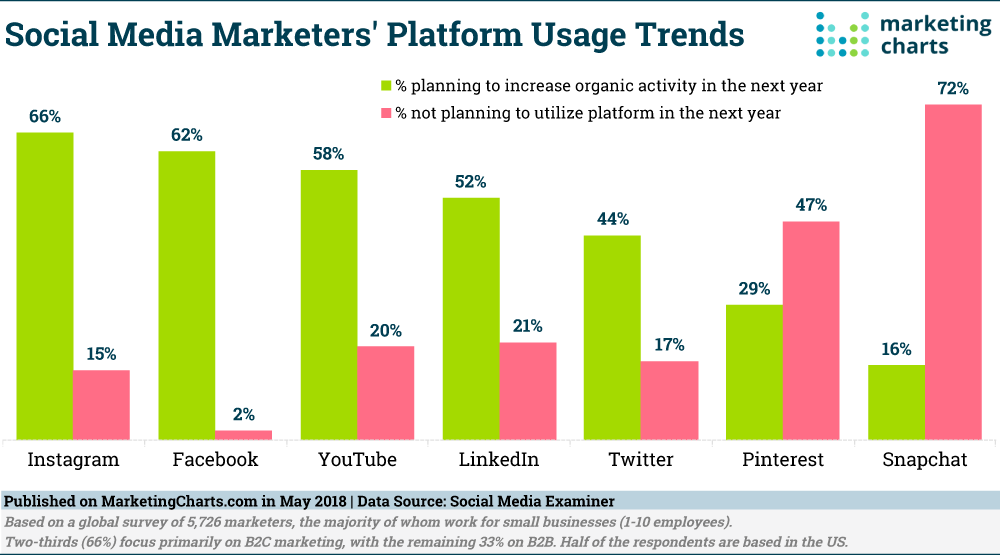
Using Facebook for Social Media Marketing
Facebook is a place where people go to relax and chat with friends, so consider a cost effective Facebook ad strategy which can have a big impact.
Using Pinterest for Social Media Marketing
Pinterest is making trends in the social media market. Pinterest’s image-centered platform is very good for retail, but almost anyone can benefit from using Pinterest for social media purposes.
Using YouTube for Social Media Marketing
YouTube is the number one place for creating and sharing video content, and it can also be used as an incredibly powerful social media marketing tool.
SCIENTIFIC COMPUTING
Scientific Computing is the collection of tools, techniques, and theories which are required to be solved on a computer.
Most of these tools, techniques, and theories were originally developed in Mathematics and many of them come long before the introduction of electronic computers.
This set of mathematical theories and techniques is called Numerical Analysis and constitutes a major part of scientific computing.
Many of the numerical methods that had been developed for the purpose of hand calculation had to be revised and sometimes abandoned. Consideration that where irrelevant or unimportant for hand calculation now became of utmost importance for the efficient and correct use of a large Computer System.
Many of these considerations such as programming languages, operating systems, management of large quantities of data, correctness of programs all were put under the new discipline of Computer Science, on which scientific computing now heavily depends. Mathematics still continues to play a vital role in scientific computing because it provides the language for the mathematical models that are solved and information about the availability of a model and it provides the theoretical foundation for the numerical strategies and, increasingly, many of the tools from computer science.
VIDEO GAME DEVELOPMENT
Video game development is the field that consists of many aspects involved in creating a video game. Every video game needs a concept, storyline, graphic design and to make the public release of the product.
Video game development is a very vast field; it is a combination of game production and game design and requires skills from both fields forming the core of a video game developer’s knowledge.
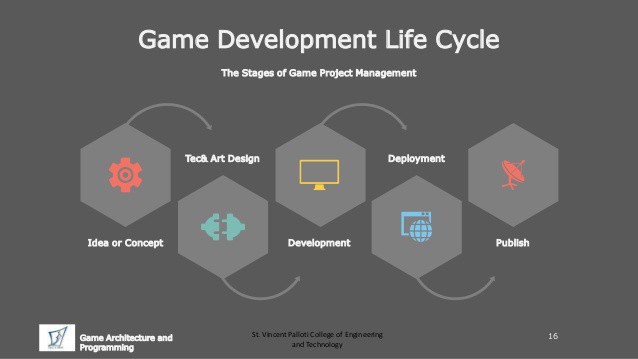
A video game developer usually holds a big position in the creation of a video game, who guides the project through multiple phases.
A video game developer is a mixture of a producer and a programmer, they are coordinating administrator with a great vision who also possess the technical skill to overcome and they also contribute to software engineering, editing and other aspects of game design.
Roles of a Development Team
- Game Producer
- Game Artist
- Programmer
- Graphic Designer
- Creative Writer
- Storyline Editor
- Audio Specialist
- Level Designer
DATA SCIENCE
Data science is a blend of data inference, algorithm development, and technology to solve analytically complex problems which arise in day to day situations. The ultimate goal of Data science is to use this data in creative ways to generate business value.

Data Science – discovery of data insight
This aspect of data science is all about uncovering what we find from the data. It is about understanding complex behaviours, trends, and inferences. It’s about surfacing hidden insight that can help enable corporations to make smarter business moves.
For example:
Netflix data mines movie viewing patterns to understand what drives user interest, and uses that to make decisions on which Netflix original series to produce.
Data Science- development of data product
A “data product” is a technical asset that:
(1) makes use of data as input, and
(2) processes the data that was taken as input to return algorithmically-generated results.
The example of a data product is a recommendation engine, which takes in user data, and makes personalized recommendations based on the data provided. For eg.
Amazon’s recommendation engines suggest what items you should buy which are determined by their algorithms. Similarly, Netflix recommends movies to you and Spotify recommends music.
Requisite Skill Set:
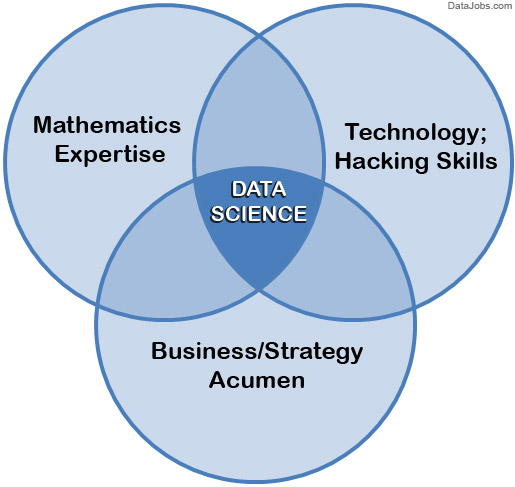
Mathematics Expertise
At the heart of mining data insight and building data product there is the ability to view the data. There are many textures, dimensions, and correlations in data which can be expressed mathematically. Solutions to many business problems involve building analytic models, where being able to understand the underlying mechanics of those models.
Technology and Hacking
Here hacking does not mean breaking into computers, it means creativity in using technical skills to build things and find clever solutions to problems.
Why is hacking ability important?
Because data scientists utilize technology in order to wrangle enormous data sets and work with complex algorithms, and it requires tools far more sophisticated than Excel.
Major languages associated with data science are SQL, Python, R, and SAS. Some other languages which are Java, Scala, Julia, and others.
Strong Business Acumen
It is very important for a data scientist to be a business consultant. As data scientists work so closely with data they can understand the data in ways no one else can. This creates the responsibility to share knowledge with others, and thus contribute to strategize on how to solve core business problems. Having this business acumen is just as important as knowing algorithms. There has to be clear distinction between data science projects and business goals.
So I would like to conclude by saying anyone who is interested in working for IT firm in the near future should learn one of the skills mentioned. Nowadays most companies are not looking from where you have studied or what is your CGPA, they are looking for what you can bring to the table.



