A kind of monetary policy which government uses to infuse money into the economy is known as quantitative easing.
This policy is used by the government to stimulate economic growth by giving a rise in bank liquidity and reducing interest rates.
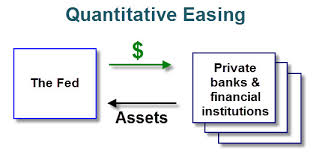
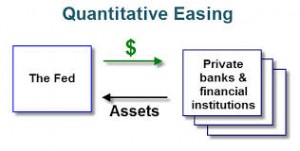
How does this policy work? The central bank creates money to purchase government securities from commercial banks and financial institutions and thereby, increasing money supply to make it possible for the commercial banks to hold cash reserves and thus to encourage banks to increase their lending activities to boost spending by the public and creating jobs. When the central bank buys the bonds, it results in the increase in the price of bonds and so brings a reduction in the interest rates.
This policy results in the increase in the economic growth of a country. But such situation may arise when this policy becomes unproductive. When the interest rates tend to approach zero, this brings ineffectiveness into the policy. Moreover, if the money supply increases too rapidly or if the commercial banks do not respond by increasing lending activities and holding the amount generated by selling securities to the central bank in their reserves, it results in the inflation in the economy.
Click here for government certification in Accounting, Banking & Finance



7 Comments. Leave new
Unique concept..Good one
Perhaps I felt that one must mention about the quantitative and qualitative measures before telling about quantitative easing. Nevertheless good efforts!
good concept..!
good one.
Nice concept.. well done..
Got something new to read
Good work 😀
A bit more livily presentation expected 😀
would have been better if you have introduced some live example 😀
nice one