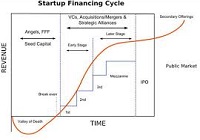
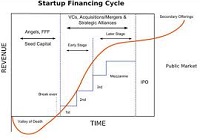
“Death Valley Curve” is a jargon used in start-up financing referring to the period during the initial investment in a start-up when the firm is not generating sufficient revenues to meet the expenses, and could be paralyzed unless they raise more capital. In short, it is the financial risk faced by start-ups to survive the initial years of their business, and become profitable in the future.
The dip of the curve shows the negative values of the balance sheet. A new firm should always maintain focus on formulating strategies, so as to cross the valley of death, and to survive, in the future. One of the major reasons behind the sudden death of start-up firms, in the initial stages of the business, is the shortage of funds. The start-ups lose their sheen within a period of 3 years, mainly due to a flawed business model.
For e.g. Taggle was a ‘group buying’ e-commerce site launched in 2010 in India, with an initial funding of Rs 5 crores from international equity funds Greylock Partners and Battery Ventures. It couldn’t survive and was shut down after a period of 1 year. The reason attributed to the closure was the increasing cost of operation and an unsustainable business model. The concept of Death Valley is synonymous with a firm breaking even, where the firm is neither making a profit, nor a loss.
So, how can a company survive the phase of Valley of Death?
- Adequate Planning of Funds (Self-funding)
The entrepreneur should have clarity in his mind regarding the various expenses which would be incurred during the formative stages of the business. An entrepreneur should accumulate some funds from his side, which can act as a safety fund during emergencies. He should invest this safety fund in an appropriate risk less instrument outside the business, and earn returns on it. This will help to mitigate the risk to a small extent.
- Alternative Source of Cash Flow
If a start-up entrepreneur is already having a job, it is advisable to hold on to the job, given that he can manage both at once, this would provide him with an alternative source of cash flow.
- Funds from Family and Friends
After Self-funding, the next viable option is family and friends. Venture Capitalists may be hesitant in investing further funds into the business. Family and Friends could be of major help during such turbulent times
- Crowd Funding
Crowd funding is an emerging area which is getting considerable attention. In India, sites such as catapooolt.com, kickstarter.com, etc. provide an opportunity, to solicit funds online. The most successful story of Crowd funding was the Kannada movie “Lucia”. The movie was funded by 100 investors and the director was able to raise Rs 51 lakhs in 10 days. Once the film starts earning profit, the investors will be getting returns on their investment.
- Bank finance
If a start-up firm has sufficient collateral to back the loan, this source could be used for a short time. While deciding to lend, banks will look at the feasibility of the business in terms of the business plan and the assets held by the business.
- Join a start-up incubator
A start-up incubator is a company, university, or other organization which provides equity funding to set up and nurture start-up firms, helping them to survive and grow during the start-up period when they are most vulnerable to risks of pre-mature closure.
- Joint venture with distributor or beneficiary
The start-up firm can join hands with an interested company such as a distributor or a supplier who would be willing to enter into long term contracts, and which would provide great opportunity to the supplier or distributor negotiate favorable price and terms. This provides stable funding to the business but also potentially provides foothold to parties who may attempt a buy out in the future. Such funding could lower the cost of goods sold or cost of providing services thereby improve profitability, pivotal in the early years of a start-up.
- Commit to a large customer
During the initial stages of the business, the company can enter into deals with a single large customer, depending upon the type of product, and could generate sufficient revenues. If the customer is impressed with the performance, could place more orders and a payment of advances. This could create dependence on small number of customers which also could threaten the business. The start-up would need to rapidly broad base the customer base soon after it breaks even.
Overcoming the valley of death shows the viability of the core business model and the ability to act to generate profits. It shows the true grit of the entrepreneur, who has the courage to take risks with a clear vision of his business. Overall, crossing the valley of death requires timely and robust planning around a fundamentally sound business model coupled with the ability to take and manage risks.
Click here for government certification in Accounting, Banking & Finance



5 Comments. Leave new
very well written
Good work
Nice article!
nicely written..
Worth reading!