Basic Probability
Let’s understand the Basic Probability. The Basic probability concepts and terminology is discussed below,
Basic Probability- 1. Probability
- The probability is the chance that something will occur and refers to a decimal fraction or a percentage.
- Moreover, it is the ratio of the chances favoring an event to the total number of chances for and against the event. That is to say, the probability is the number of successes divided by the total number of possible occurrences.
2. Sample Space
- It is the set of possible outcomes of an experiment or the set of conditions. Moreover, it is denoted by the capital letter S. And, sample space outcomes are in lower-case letters (a, b, c . . .) or the actual values like for a dice, S={1,2,3,4,5,6}.
3. Event
- Event is a subset of a sample space and is denoted by a capital letter such as A, B, C, etc. Moreover, events have outcomes, which are lower-case letters (a, b, c . . .) or the actual values if given like in rolling of dice, S={1,2,3,4,5,6}. Then, for event A if dice shows 5 so, A ={5}. The sum of the probabilities of all possible events in total sample space is equal to 1.
4. Independent Events
- Each event does not affect any other events. For example, tossing a coin three times and it comes up “heads” each time. That is to say, the chance that the next toss will also be a “Head” is still 1/2 as every toss is independent of earlier one.
5. Dependent Events
- They are the events that affect previous events like drawing 2 Cards from a deck that will reduce the population for the second card. And, the probability after taking one card from the deck there are fewer cards available. So, as the probability of getting a King, for the 1st time is 4 out of 52 but for the 2nd time is 3 out of 51.
7. Simple Events
- An event that does not decompose is a simple event (E). Moreover, the set of all sample points for an experiment is called the sample space (S).
8. Compound Events
- Compound events is a composition of two or more events. Moreover, the two most important probability theorems are the additive and multiplicative laws.
9. Union of events
- The union of two events is that event consisting of all outcomes in either of the two events. Moreover, the union is known by the symbol U place between the letters indicating the two events.
10. Intersection of events
- The intersection of two events is that event consisting of all outcomes that the two events have in common. In the same vein, it can also be referred to as the joint occurrence of events.
- Moreover, the intersection is known by the symbol ∩ placed between the letters indicating the two events like for event A={1,2} and event B={2,3} then, A∩B = {2}.
11. Complement
- The complement of an event is the set of outcomes in the sample space that are not in the event itself. And, the complements are shown by the symbol that is after the letter indicating the event like for event A={1,2} and Sample space S={1,2,3,4,5,6} then A`={3,4,5,6}
12. Mutually Exclusive
- Mutually exclusive events have no outcomes in common like the intersection of an event. And, its complement contains no outcomes or it is an empty set, Ø for example if A={1,2} and B={3,4} and A ∩ B= Ø.
13. Equally Likely Outcomes
- When a sample space consists of N possible outcomes, all equally likely to occur, then the probability of each outcome is 1/N.
- For example, the sample space of all the possible outcomes in rolling a die is S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, all equally likely. And, each outcome has a probability of 1/6 of occurring but, the probability of getting a 3, 4, or 6 is 3/6 = 0.5.
14. Conditional probability
- Conditional Probability is the result of an event depending on the sample space or another event. And, the conditional probability of an event can be found as.
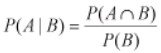
Learn and enhance your knowledge about basic probability. Become a Certified TQM Professional Now!

