The diversity of information content and the numerous sharing options makes it seemingly impossible to classify the nature or level of information sharing. Our field studies have indicated that a number of different sharing arrangements are possible. For example, some suppliers share inventory position information of the products a certain supplier sells them. This information may be transmitted daily, or weekly; the level of detail also varies. There are suppliers who see the store-level day- to-day point-of-sales (POS) information; there is a great deal of variety here as well – some see only product UPC’s and quantities, while others have access to temporal sales distribution and customer profiles. Other buyers transmit order quantity, payment and cost information using EDI – this is a situation where the volume of information exchanged may be great, but its impact on the operations of the firms is relatively low.
If one examines information from another perspective, the problem simplifies a great deal. Treat the level of information shared not based on what its exact content or volume is, but rather, based on the impact it has on the operations, sales, marketing and production strategies of the parties that contract to share the information. Using this view, one can classify IOIS arrangements into four categories, based on the level of impact the shared information has on the buyer and supplier (Figure 1).
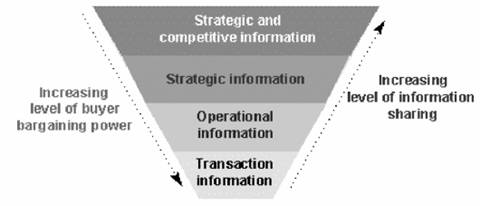
Figure 1: Models of information sharing
The first level involves increased cost-and-time-effective exchange of transaction-level information (like order quantities and prices) through EDI. The second level involves sharing select operational information (such as inventory levels) in order to exploit superior expertise across organizational boundaries, and improve operating efficiency. At the third level, the information shared has strategic value to the party that receives the information. Finally, at the highest level, the information adds both strategic and competitive value to the party that receives it.
Exchanging Order Information: Many IOIS arrangements do not involve sharing firm-specific operations information; they merely improve logistics processes through efficiency gains from EDI. We treat this case – where the companies exchange ordering information – as our base case. (Figure 2)
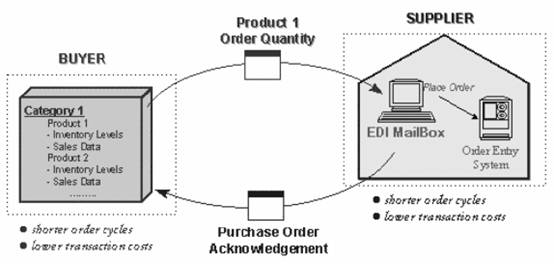
Figure 2: EDI — exchanging transaction information
This is one of the oldest and most widely prevalent forms of IOIS, and is aimed at reducing transactions costs and the duration of order cycles.
At this level, both parties gain from reduced order cycle times (which reduce inventory levels). The value gained is not joint; each party improves efficiency independently, and hence there are no value sharing issues. There is the issue, however, of information technology costs. One party may find it cost- effective to invest in an EDI system that enables these improvements; the other may not. However, both need to invest in the system in order to transact electronically.
Sharing Operations Information
Information is often shared to leverage on the superior expertise, or operational economies-of-scale of one organization. This occurs when one firm owns valuable information, while the other firm possesses the ability to use this information. An example of this is vendor managed inventory (Figure 3).
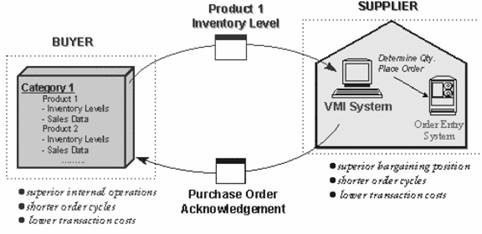
Figure 3: VMI — sharing operational information
For instance, a buyer shares aggregate inventory position information with its suppliers; this enables suppliers to manage the inventory of their own products at the buyer’s site. Suppliers are better equipped to perform these duties, for the following reasons:
- They have experience managing large supply side inventories of this product.
- They have superior knowledge of production schedules, which reduces the supply-side uncertainty that a buyer normally faces, resulting in a lower average inventory for the buyer.
- They could have comparable VMI arrangements with a number of buyers (economies-of-scale).
Efficiency gains are not restricted to inventory cost reductions. In our case in when product specifications, packaging specifications or packaging quantities changed, an order sent with an outdated UPC would generate rework. When new products were introduced, there was a similar problem. Moving to VMI eliminated these difficulties. However, the buyer’s costs of ordering and order fulfillment are now borne by the supplier.
What does the supplier gain? Their internal operating efficiency gains are minimal at best. However, one benefit that may not be immediately tangible (if it exists) is that the supplier’s relative bargaining position for its transactions with the buyer may improve. Since it is has superior knowledge of how well or badly its product is doing on a regular basis, the information asymmetry it faces reduces; it may therefore be able to bargain for price schedules that are more favorable.
It is likely that the contracts underlying these sharing agreements will include value sharing agreement between the buyer and the supplier. Alternately, there could be a penalty for non-VMI suppliers. This penalty could range from a complete shut-out (‘we do business only with suppliers who manage their own inventories in our stores’ – implies a strong bargaining position on the buyer side, despite the apparent gain in power by the supplier as described in the previous paragraph) to some kind of price advantage that the buyer passes on to the supplier. Our discussion in provides insight into some these issues.
Sharing Strategic Marketing Information
It is becoming common for organizations to share brand- specific information which provides strategic benefits to one of the organizations, and also leverages on their superior expertise This occurs when one organization owns information that it can derive little independent value from, but which another can use to generate operational benefits for the company it receives the information from, besides garnering strategic value for its own sales and marketing departments. For instance, a retailer possesses POS (point-of-sales) information on all the products it sells. This information is not of much value in isolation; however, a supplier can make superior demand forecasts by analyzing detailed transaction level information from many retailers. This form of information sharing is used in the efficient customer response, continuous replenishment and quick response systems models (Figure 4), common in the grocery and fashion retailing industry. ).
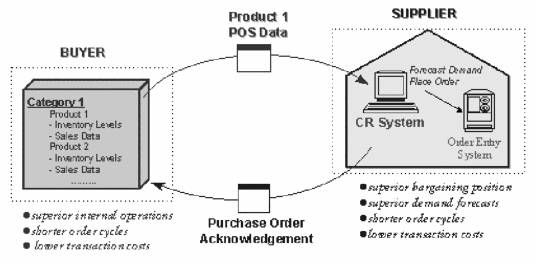
Figure 4: Continuous Replenishment — sharing strategic information
The model has been discussed for many years now – supply chain management has always striven to move towards a system where consumer purchases ‘pull’ goods through the chain, rather than suppliers ‘pushing’ them.
Since inventory positions can easily be derived from POS information, the operational information is also being shared. Hence, all the benefits that accompany VMI-type situations still exist. However, this information is of a much higher level of detail than inventory aggregates. – it can be used by the supplier’s sales and product development groups for improved demand forecasting, promotion scheduling and segment- specific forecasts. According to the director of worldwide sales forecasting at Eastman Kodak, such region specific and tactical demand forecasts are increasingly becoming a major role of sales. Reduced demand uncertainty also improves the internal inventory management of the supplier.
The benefits described above may indicate that the buyer can induce suppliers unwilling to enter into information sharing agreements by offering them access to information that is of strategic value. However, when this information is available to the supplier, the relative bargaining power of the buyer is reduced further. For instance, in the POS example above, the supplier now knows not only gross product movement figures, but also the details of what prices the buyer charges consumers, any local demand patterns and the schedule of promotions – this puts the buyer at a significant disadvantage when negotiating supply terms.
Sharing Strategic and Competitive Marketing and Sales Information: At the highest level of information sharing, it is possible for a buyer to allow a supplier to access broad market information that provides the supplier with strategic and competitive benefits This occurs when one organization possesses information that it can derive little independent value from, but from which another can derive internal strategic production benefits, as well as competitive sales and marketing benefits. The competitive benefits are with respect to intra-industry rivals – this information does not give the supplier additional competitive advantage over the buyer, but over other suppliers in its own industry. Category management is an example of this situation (Figure 5).
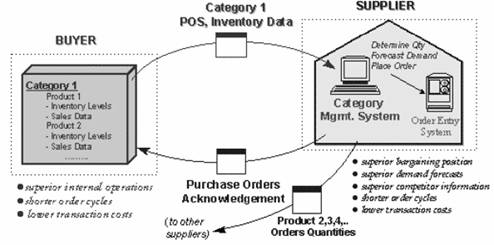
Figure 5: Category management — sharing strategic and competitive marketing information
The retailer endows one of the suppliers with inventory management responsibility over all the products supplied for that category, and provides them with the relevant POS information. This gives that supplier strategic benefits (from improved demand forecasts), competitive benefits (from sales and demand information about competitor’s products), and will enable superior inventory management. It also reduces the buyer’s operating costs tremendously – not only are all order management costs eliminated, but the buyer deals with only one supplier per category, and hence have a significant reduction in information technology costs.
On the face of it, the supplier also gains tremendously when provided access to this information. Not only are all the benefits of present, but the supplier can track the sales of competing products in the category, and use this information to improve the sales strategy of their own product. Since there may be a time lag between the category manager generating an order, and a competing supplier receiving it, inventory costs of competing products will tend to be higher, and hence the category manager gains a cost advantage as well. The tradeoff appears to be increased transaction costs for the supplier, who manages orders and monitors product movements of a whole category of products.
Summary and Insights
Corporations have long been aware of how information systems can allow them to operate across organizational boundaries; however, there has not been much research into the competitive implications of these IOIS arrangements. There has also been significant concern on the part of suppliers who see no tangible benefits accruing to them from different information sharing arrangements. Our study offers the following insights into these long-standing concerns.
- The impact of IOIS relationships is not merely operational; they can alter supplier marketing and sales strategies, and shape competition in supplier markets.
- It is possible for a buyer to extract all the competitive value of information from each supplier. Therefore, it is worthwhile for buyers to collect as much information as possible that is of competitive value to their suppliers – they need not actually share it – a realistic threat of potential sharing is sufficient.
- In a supplier market with many competing suppliers of similar size, VMI is likely to be the best policy for a buyer; though category management may offer higher operational savings, a buyer can do better by extracting competitive value from the suppliers with the threat of CM.
- The following factors increase the operational savings that a supplier expects from an IOIS relationship:
- High inventory cost rates
- High demand uncertainty
However, the supplier should examine the competitive factors involved in these arrangements, before being tempted by large (and often illusory) cost savings, as the buyer could end up getting all the value from the arrangements.
- Buyers should target suppliers who have the characteristics described in (4), as they are likely to be tempted by the prospects of high savings – since these savings are likely to accrue to the buyer; these are better firms to share information with. The same holds for highly competitive supplier markets.
- Partnering with suppliers (as advocated by many supply chain management information systems vendors) is unlikely to be optimal for the buyer in many situations. There is little reason for buyers to be worried about loss in bargaining power when they share information; through creative contracting, they can regain any power they apparently lose.
- A supplier in an IOIS relationship is unlikely to benefit from the relationship, or accrue any of the value generated; however, it may still be necessary to remain in the arrangement, to avoid further losses. A supplier who breaks even on a VMI or category management agreement, is probably doing as well as they can.
- As I.T. enables buyers to use and share information more effectively, they will ‘pull’ more and more from suppliers. Hence, suppliers may do well to negotiate long-term VMI contracts with buyers. If a buyer possesses competitive information that is potentially very valuable to a supplier; it is a predictor of all suppliers losing a lot.
- As the cost of processing and sharing information drops, as is evidently has and will continue to do, two related occurrences are very likely:
- The volume of information that a buyer collects (and can potentially share) will increase
- The strategic and competitive value of this information to suppliers will increase

