Single Purpose Aggregation Operations
Aggregation refers to a broad class of data manipulation operations that compute a result based on an input and a specific procedure. MongoDB provides a number of aggregation operations that perform specific aggregation operations on a set of data. Although limited in scope, particularly compared to the aggregation pipeline and map-reduce, these operations provide straightforward semantics for common data processing options.
Count – MongoDB can return a count of the number of documents that match a query. The count command as well as the count() and cursor.count() methods provide access to counts in the mongo shell. As an example, given a collection named records with only the following documents:
{ a: 1, b: 0 }
{ a: 1, b: 1 }
{ a: 1, b: 4 }
{ a: 2, b: 2 }
The following operation would count all documents in the collection and return the number 4:
db.records.count()
The following operation will count only the documents where the value of the field a is 1 and return 3:
db.records.count( { a: 1 } )
Distinct – The distinct operation takes a number of documents that match a query and returns all of the unique values for a field in the matching documents. The distinct command and db.collection.distinct() method provide this operation in the mongo shell. Consider the following examples of a distinct operation:
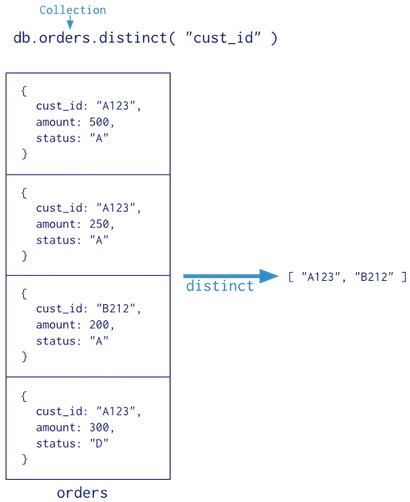
Diagram of the annotated distinct operation.
As an example, given a collection named records with only the following documents:
{ a: 1, b: 0 }
{ a: 1, b: 1 }
{ a: 1, b: 1 }
{ a: 1, b: 4 }
{ a: 2, b: 2 }
{ a: 2, b: 2 }
Consider the db.collection.distinct() operation which returns the distinct values of the field b
db.records.distinct( “b” )
The results of this operation would resemble
[ 0, 1, 4, 2 ]Group – The group operation takes a number of documents that match a query, and then collects groups of documents based on the value of a field or fields. It returns an array of documents with computed results for each group of documents. Access the grouping functionality via the group command or the db.collection.group() method in the mongo shell. group does not support data in sharded collections. In addition, the results of the group operation must be no larger than 16 megabytes. As an example, given a collection named records with the following documents
{ a: 1, count: 4 }
{ a: 1, count: 2 }
{ a: 1, count: 4 }
{ a: 2, count: 3 }
{ a: 2, count: 1 }
{ a: 1, count: 5 }
{ a: 4, count: 4 }
Consider the following group operation which groups documents by the field a, where a is less than 3, and sums the field count for each group
db.records.group( {
key: { a: 1 },
cond: { a: { $lt: 3 } },
reduce: function(cur, result) { result.count += cur.count },
initial: { count: 0 }
} )
The results of this group operation would resemble the following
[{ a: 1, count: 15 },
{ a: 2, count: 4 }
Apply for MongoDB Certification Now!!
https://www.vskills.in/certification/databases/mongodb-server-administrator

