Certify and Increase Opportunity.
Be
Govt. Certified Marketing Manager
Retailing, Wholesaling, and Logistics
RETAILING
Includes all the activities in selling goods or services directly to final consumers for personal. Does not matter if the organization is a manufacturer, wholesaler, or retailer; if it is selling to final consumers, is doing retailing. Besides that, does not matter how the goods or services are sold (in person, by mail, telephone, vending machine, or on the Internet) or where (in a store, on the street, or in the consumer’s home).
Types of Store Retailing:
- Specialty store: narrow product line.
- Department store: several product lines.
- Supermarket: large, low-cost, low-margin, high-volume, self-service store designed to meet total needs for food and household products.
- Convenience store: small store in residential area, limited line of high-turnover convenience products.
- Discount store: standard or specialty merchandise; low-price, low-margin, high-volume stores.
- Off-price retailer: leftover goods, overruns, irregular merchandise sold at less than retail.
- Superstore: huge selling space, routinely purchased food and household items, plus services.
- Catalogue showroom: broad selection of high-markup, fast-moving, brand-name goods sold by catalogue at discount. Customers pick up merchandise at the store.
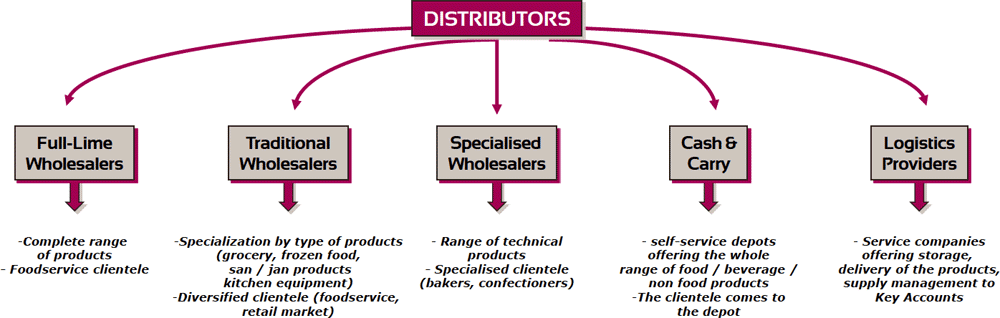
WHOLESALING
Wholesaling includes all the activities in selling goods or services to those who buy for resale or business use. It excludes manufacturers and farmers because they are engaged primarily in production, and it excludes retailers. Major type of retailers:
- Merchant wholesalers: Independently owned businesses that take title to the merchandise they handle. They are full-service and limited-service jobbers, distributors, mill supply houses.
- Full-Service wholesalers: Carry stock, maintain a sales force, offer credit, make deliveries, provide management assistance. Wholesale merchants sell primarily to retailers.
- Limited-service wholesalers: cash and carry wholesalers sell a limited line of fast-moving goods to small retailers for cash.
- Brokers and agents: facilitate buying and selling, on commission of 2% to 6% of the selling price; limited functions; generally specialize by product line or customer type. Brokers bring buyers and sellers together and assist in negotiation; paid by the party hiring them. Agents represent buyers or sellers on a more permanent basis.
- Manufacturers and retailers branches and offices: Separate branches and offices are dedicated to sales or purchasing. Many retailers set up purchasing offices in major market centers.
- Specialized Wholesalers: Wholesalers specialized in one area. Agricultural, Petroleum, etc.
LOGISTICS
Physical distribution has been expanded into the broader concept of supply chain management (SCM). SCM involves procuring the right inputs; converting them efficiently into finished products; and dispatching them to the final destination.
Market logistics includes planning the infrastructure to meet demand, then implementing and controlling the physical flows of materials and final goods from points of origin to points of use, to meet customer requirements at a profit. Studying market logistics leads managers to find the most efficient way to deliver value. It has four steps:
- Deciding on the company’s value proposition to its customers.
- Deciding on the best channel design and network strategy for reaching the customers.
- Developing operational excellence in sales forecasting, warehouse management, transportation management, and materials management.
- Implementing the solution with the best information systems, equipment, policies, and procedures.
Apply for Marketing Manager Certification Now!!
http://www.vskills.in/certification/Certified-Marketing-Manager

