The level of investment in current assets determines the working capital policy. A business firm can adapt any of the following working capital policies:
- Conservative working capital policy
- Aggressive working capital policy
- Moderate working capital policy
Under Conservative approach, the firm carries high investment in current assets such as cash, marketable securities and carries large amount of inventories and grants generous terms of credit to customers resulting in a high level of debtors. The consequences of conservative working capital policy are quick deliveries to customers and more sales due to generous credit terms.
Under Aggressive working capital policy, investment in current assets is very low. The firm keeps less amount of cash and marketable securities, manages with less inventories and tight credit terms resulting in low level of debtors. The consequences of aggressive working capital policy are frequent production stoppages, delayed deliveries to customers and loss of sales.
A tradeoff between two costs namely carrying cost and shortage cost determines the optimal level of current assets. Costs that rise with current assets i.e. that cost of financing a higher level of current assets form carrying costs. Shortage costs are in the form of disruption in production schedule, loss of sales and loss of goodwill.
The optimum level of current assets is denoted by the total costs (= carrying costs + shortage costs) minimized at that level.
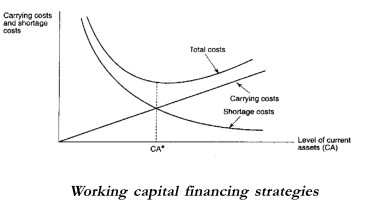
After determining the level of current assets, the firm must determine how these should be financed.
Investment in current assets can be broken into two parts
- Permanent current assets
- Temporary current assets
A firm requires a certain amount of current assets to meet even the minimum level of sales where as temporary current assets reflects a variable component that moves in line with seasonal fluctuations. Several strategies are available for financing capital requirements.
The fixed proportion of working capital should be generally financed from the fixed capital sources while the temporary or variable working capital requirements of a firm may be met from the short term sources of capital. Based on this idea, we have 3 strategies possible.
- Strategy A – Long term financing is used to meet fixed asset requirement as well as peak working capital requirement. When the working capital requirement is less than its peak level, the surplus is invested in liquid assets(cash & marketable securities)
- Strategy B – Long term financing is used to meet fixed asset requirements, permanent working capital requirement, and a portion of fluctuating working capital requirement. During seasonal upswings, short term financing is used. During seasonal downswings, surplus is invested in liquid assets.
- Strategy C – Long term financing is used to meet fixed asset requirement and permanent working capital requirement. Short term financing is used to meet fluctuating working capital requirement.

