Wind energy is the kinetic energy of large masses of air moving over the earth. Because the sun heats the earth’s surface and atmosphere unevenly, thermal differences produce air density and pressure differences and drive air masses around the planet. The earth’s rotation also contributes to powerful air currents.
A wind energy conversion system (WECS) converts this kinetic energy into mechanical energy and electrical energy using airfoils , a drive train, and a generator. The conversion process begins as air flows over a blade, called an airfoil that is similar to an airplane wing or propeller.
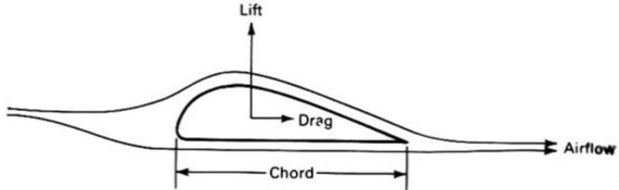
Airflow over a stationary airfoil produces two forces, a lift force perpendicular to the airflow and a drag force in the direction of airflow, as shown in figure below. The air flowing over the top of the airfoil has to speed up because of a greater distance to travel, and this increase in speed causes a slight decrease in pressure. This pressure difference across the airfoil yields the lift force, which is perpendicular to the direction of airflow.
Extraction of Wind Turbine Power
(Source: research paper titled “Wind energy extraction and conversion: optimization through variable speed generators and non linear fuzzy control by Paulo Costa”)
A wind turbine is characterized by its power-speed characteristics. For a horizontal axis wind turbine, the amount of power Pt that a turbine is capable of producing is given by
Pt = ½ *cp*p*a*v3
where ρ is the air density,
A is the swept area of the turbine
and v is the wind velocity.
The Cp parameter is called the power coefficient and is dependent on the ratio between the linear velocity of the blade tip (R*Wt ) and the wind velocity (v). This ratio, known as the tip-speed ratio, is defined as w R* t v λ = (2) where R is the radius of the turbine. This kind of application is designable with constant or variable speed. Different types of wind turbines are available on the market. The different types of wind turbines have their own advantages and disadvantages. Fixed-speed wind turbines normally cause a voltage drop during start-up . The voltage drop is mainly caused by reactive power consumption during magnetization of the generator. Another problem concerned to wind turbines with fixed speed is the flicker produced during normal operation of the wind turbine. Once this method the energy extraction is optimized for one point of operating, it means that for only wind speed is achieved the maximum value of extraction. The variations in the generated power are mainly caused by the wind turbines and the tower shadow effect. These variations can lead to flicker emission. Variable-speed wind turbines can reduce these power variations and eliminate the flicker caused by power pulsation, becoming possible to maximize the energy extraction using an appropriated control method.

