Strategy implementation is mostly affected by instrumental values of people in the organisation. However, when we say people, the question arises: who- are- these people in the oigamsati6n? The answer -of -this question is significant – because that will determine the shape of strategy implementation. From strategic management point of view, people ill an organisation are divided into four groups board of directors chief executives, other managers, and corporate planning staff, . Out of these groups, chief executive and managers under” him are mostly responsible for, strategy implementation. However, values are held by individuals which are part of their personality. Therefore, it is quite likely that values of different individuals do not match. Though organisational culture represents the collectivity of personal values, ‘it is only representative and not all inclusive. Thus, in actual practice, the relationship between organisational values and personal values exists as shown in Figure.
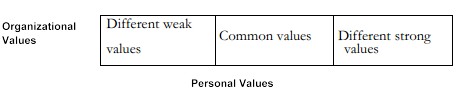
Two – sets of values-organisational and personal show following relationships ‘and reconciling; or modifying process:
Common-Values: Since an organisation is a collectivity of people and organisational values represent the collective values of its members. There are some commonalities between these two. These common values do not require any reconciliation or modification because both have already been integrated.
Different weak Values: In this case, part of the organisational and personal values differs but the divergence is related to weak values either terminal or instrumental. A weak value has low priority in the hierarchy of values whether organisational or personal. In fact, every individual has a set of values arranged in hierarchy. Because of hierarchical nature of values. They differ in terms of importance. Since there are individual differences, hierarchy of values also differs. For example, an individual may attach very high importance to honesty and integrity and does not reconcile on these issues. Another individual may place it at low level and may reconcile on these issues.
Therefore, weak and strong values are relative and person-oriented. Where divergence exists on weak values reconciliation takes place through normal socialization process which involves adaptation of organisational values and norms by employees with a view, to adhere to those. This socialization- process, however, is one-way traffic rather two-way traffic in which an individual is able to modify’ organisational values to-some extent.
Different-Strong values: Problems in ‘strategy implementation emerge when there is divergence of values which are strong for the organisation or individual. If values are strong to the organisation any divergence may lead to separation of individuals whose values are at divergence. Another alternative available to the’ organisation is to design its structure and processes in such a way that these match with the values of an ‘individual whose values are at divergence. In such a situation, the organisation will retain its core values while allowing change in others. This type of adjustment is required when the individuals are quite critical to the success of the strategy under implementation.
Corporate Governance: Corporate governance is a newly introduced ‘system for managing a company in the best interest of all its stakeholders – though in the ‘context of state administration, the concept of governance is quite old, where it is referred to as the system of directing and controlling the activities of a state particularly in princely states and empires.
Contents of Corporate-Governance Code
A corporate governance code -usually contains the following matters:
- Constitution of Board of Directors Constitution of board of directors role of non-executive directors, its meeting, key matters that must be brought before the board, etc.
- Disclosure of Information Disclosure of financial and other information in the company’s annual accounts and reports as well as periodical disclosure
- Management Practices. Management practices to protect the interests of shareholders, consumers, financiers, creditors, distributors, government and society

