Object Repository Basics
Object Repository is a collection of object and properties with which QTP will be able to recognize the objects and act on it. When a user records a test, the objects and its properties are captured by default. Without understanding objects and its properties, QTP will NOT be able to play back the scripts.
Object Repository and its associated features are briefed below
| Topic | Description |
| Object Spy and its Features | To Understand the usage of object Spy and its associated functionalities. |
| Working with Object Repository | Adding,Editing, Deleting Objects from an Object Repository and its associated functionalities. |
| Types of Object Repository | Deals with Shared Object and Local Object Repository and their context with respect to scripting. |
| User-defined Objects | Deals with the circumstances to use the User-Defined Objects. |
| Object Repository in XML | Deals with converting OR’s to XML and how to use the object Repository as XML. |
| Comparing and Merging OR | Operations such as Compare OR’, Merge OR’s to effectively work with Object Repository. |
| Ordinal Identifiers | Circumstances when the ordinal identifiers are used and their advantages. |
| Child Objects | Using Child Objects for effective scripting |
QTP Object Identification
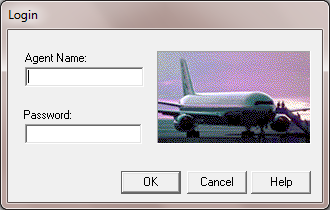
When you look at the below screen
There are 3 buttons and 2 text boxes along with various other elements in this dialog. It is clear that QTP somehow remembers which object to act on. The way it does it is, it stores the object in the AUT as a test object. It then examines its properties and classifies the object. For E.g.: when it encounters the OK button it examines its properties and based on these, it classifies the object as a ‘WinButton’.
QTP has a predetermined set of properties that it learns/stores for every class of object it identifies. There are 3 aspects to this:
- Mandatory properties: This is the list of properties for a certain class that QTP always stores. We could say that this is the object description. It also checks this in conjunction with the parent object to see if the description is sufficient to identify the object uniquely.
- Assistive properties: In case the description of mandatory properties is insufficient to identify the Object a set of non-mandatory properties will be added to the description one after the other until there is enough data to identify the object.
- Ordinal Identifier: If the assistive properties also do not result in unique identification of an object a special ordinal identifier is added by QTP, such as the object’s location on the page or in the source code.
So, this is how QTP forms Test Objects. It uses this Test Object description to search for the objects to act on during a run session. It chooses the objects that match perfectly with the description it contains. These objects are called Run-Time objects.
Unless your application has changed significantly the Test Object description that QTP has is sufficient to find an object.
Test Your Automation Testing Skills By Taking Our Free Practice Tests On This Link