Scrum technique is a type of lightweight agile method that involves practices, events, roles, artifacts, and rules for project execution.
Guiding Pillars of the Scrum Project
- Transparency: There is utmost transparency maintained on a scrum project so that it is visible to the entire stakeholder in the outcome.
- Inspection: Regular inspection of the scrum project is done to ensure a directed progress towards the end goals and objectives.
- Adaptation: Required adjustments are made in the processes as and when needed to get rid of issues and problems.
Benefits of Scrum Method
- Process is incremental and iterative
- Requirements are permitted to change over a period of time
- End users are actively involved throughout the project
- Process is straightforward and uncomplicated
Weaknesses of Scrum Methods
- In case the team member leaves the project, causing a significant impact of the project.
- Scrum project requires experienced team members therefore an inexperienced team member can lead to project delays.
- Scrum method is very informal.
Features of Scrum Methods
- Scrum project has six to ten team members
- Scrum method id best suited for companies and projects that are team, value, and customer oriented.
- Scrum approach assumes that the analysis, design, and development processes in the Sprint phase are unpredictable.
- Scrum method uses the control mechanism to manage the unpredictability and control the risk.
- Scrum method results in flexibility, responsiveness, and reliability.
Scrum Cycle
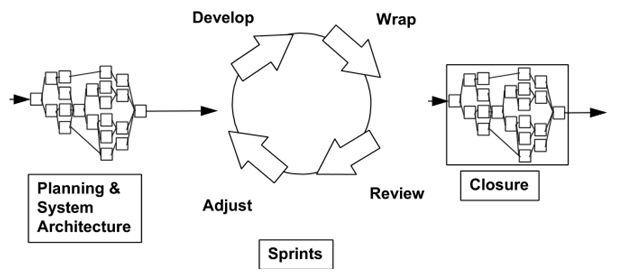
Steps in Scrum Cycle
- Step 1: Product owner creates a prioritized wish list called a product backlog.
- Step 2: During sprint planning, the team pulls a small chunk from the top of that wish list, a sprint backlog, and decides how to implement those pieces.
- Step 3: The team has a certain amount of time — a sprint (usually two to four weeks) — to complete its work, but it meets each day to assess its progress (daily Scrum).
- Step 4: Along the way, the ScrumMaster keeps the team focused on its goal.
- Step 5: At the end of the sprint, the work should be potentially shippable that is ready to handover to a customer, put on a store shelf, or show to a stakeholder.
- Step 6: The sprint ends with a sprint review and retrospective.
- Step 7: As the next sprint begins, the team chooses another chunk of the product backlog and begins working again.
The scrum cycle repeats until enough items in the product backlog have been completed, or the budget has been exhausted, or a deadline arrives. Scrum ensures that the most valuable work has been completed when the project ends.

