Ratings result from a thorough analysis of public and private information from all relevant sources. The rating process involves a quantitative analysis, which looks at the debt structure, financial statement, balance-sheet data and sector information. The qualitative analysis then looks at management quality, competitive position, and growth prospects. Information is obtained from public sources and from the rated company itself during visits and meetings with the senior management. The credit rating is assigned by a rating committee of experts on different domains and is communicated with the senior management of the issuer that requested the rating. After the first rating assignment, the rating is re-evaluated on an ongoing basis by the agency until the rating is withdrawn.
The original purpose was to distinguish between investment grade and non-investment-grade debt securities. The first credit ratings aimed to pro- vide an ordinal measure of the default or expected loss risk of the issued bond. Nowadays, credit ratings have been aligned to issuer default risk and issue loss or recovery risk. The information is gathered on a confidential basis and assessed with a view to examine the capacity of the company to service the instruments issued to the public.
Broadly, there are three categories of ratings:
- Long-term Instruments (Debentures and Preference Shares) Triple A to triple B
- Medium-term Instruments (Fixed Deposits) FAAA to FA
- Short-term Instruments(C.P., etc.) PI + to P3
The rating indicates the degree of risk and the highest safety possible is under the rating of AAA or FAAA or PI’. The credit worthiness is indicated in the ratings and reflects the capacity of the company to service them adequately with a view to ensure the timely payment of interest and principal.
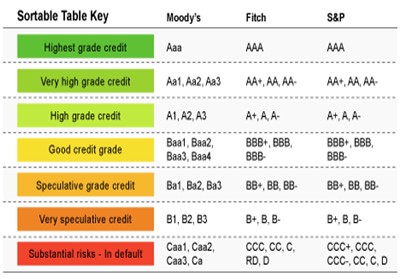
Default ratings are the most commonly used type of credit ratings and it measures the relative default risk of an issuer in terms of the probability of default (PD). Different agencies use different definitions of default. These definitions are usually based on the occurrence of a delayed payment of interest and/or principal on any financial obligation. The definitions may differ on the method of treatment of missed payments made during a grace period or missed payments because of commercial disputes.
Advantages
It will help raise funds in the capital market. Although many companies have got their instruments evaluated by rating agencies, to get an independent view of their credit standing, a few only have publicised them. For the investors these rating help them in making a decision of their investment in various instruments. Such ratings have a demonstration effect and improve competitiveness of the companies to outperform each other.

