During the 80s era, the MRP technology was enhanced to formulate a new approach, known as MRP (Manufacturing Resource Planning) II that encompassed techniques to facilitate providing valid production schedules that further enables better planning and control of other resources. Often the areas of finance, marketing and human resources get affected by any improvements in customer delivery commitments, HR management projections and cash flow projects. The invention of MRP II has not replaced MRP, or is an improved version of MRP, but it does expand the scope of production resource planning and engages other functional areas, such as finance, marketing, purchase, HR and engineering, in the planning stage of an organization. In MRP II, the functional areas are inputs to the master production schedule. With this, MRP generates material requirements through which production managers plan the capacity. MRP II systems generally consist of simulation capabilities for the managers to be able to assess alternate options.
In the MRP II (or MRP2) concept, fluctuations in forecast data are taken into account by including simulation of the master production schedule, thus creating a long-term control. A more general feature of MRP2 is its extension to purchasing, to marketing and to finance (integration of all the function of the company), ERP has been the next step.
Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) is an integrated information system used by businesses. Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) evolved from early Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) systems by including the integration of additional data, such as employee and financial needs. The system is designed to centralize, integrate and process information for effective decision making in scheduling, design engineering, inventory management and cost control in manufacturing.
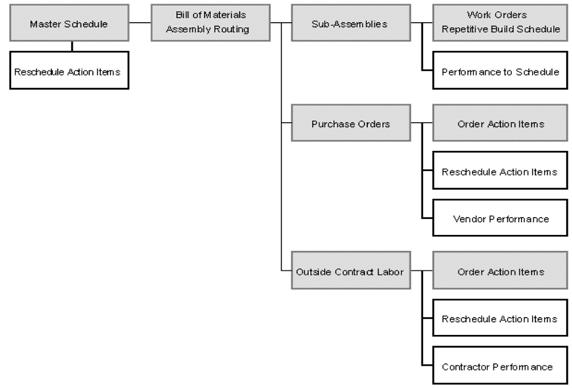
Manufacturing resource planning (MRP II) is an integrated method of operational and financial planning for manufacturing companies. MRP II serves as an extension of MRP (closed loop manufacturing resource planning, also abbreviated as CLMRP).
The typical MRP II system employs a modular organizational structure. Modules keep track of, and regulate, specific characteristics and functions of the entire organization. Examples include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Product design
- Product specifications
- QC (quality control)
- QA (quality assurance)
- Shop floor control
- Order management
- Purchasing
- Inventory
- Cost calculation
- Cost reporting
- General accounting
- Cash flow
- Tax calculation
- Tax payments
The MRP II process is carried out by a synergistic combination of computer and human resources. The MRP II differs fundamentally from point contact planning, in which individual characteristics and functions have their own dedicated systems.
The MRP II system integrates these modules together so that they use common data and freely exchange information, in a model of how a manufacturing enterprise should and can operate. The MRP II approach is therefore very different from the “point solution” approach, where individual systems are deployed to help a company plan, control or manage a specific activity. MRP II is by definition fully integrated or at least fully interfaced.
- MRP II systems can provide:
- Better control of inventories
- Improved scheduling
- Productive relationships with suppliers
MRP II systems have been implemented in most manufacturing industries. Some industries need specialised functions e.g. lot traceability in regulated manufacturing such as pharmaceuticals or food. Other industries can afford to disregard facilities required by others e.g. the tableware industry has few starting materials – mainly clay– and does not need complex materials planning. Capacity planning is the key to success in this as in many industries, and it is in those that MRP II is less appropriate.
This is not exclusively a software function, but a marriage of people skills, dedication to data base accuracy, and computer resources. It is a total company management concept for using human resources more productively.

