Financial leverage can be defined as the degree to which a company uses fixed-income securities, such as debt and preferred equity. With a high degree of financial leverage come high interest payments. As a result, the bottom-line earnings per share is negatively affected by interest payments.
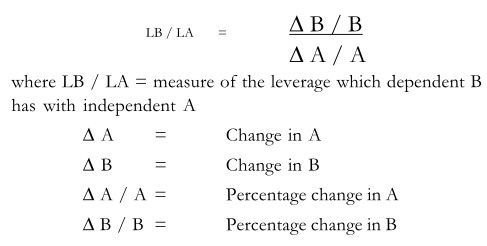
In financial analysis, leverage represents the influence of one financial variable over some other related financial variable. Leverage in the general sense means influence of power i.e., utilizing the existing resources to attain something else. Leverage in terms of financial analysis is the influence which independent financial variable has over a dependent / related financial variable. These financial variables may be costs, output, sales revenue, Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT), Earning per share (EPS) etc. When leverage is measured between two financial variables it explains how the dependent variable responds to a particular change in the independent variable. To explain further, let A be an independent financial variable and B its dependent variable, then the leverage which B has with A can be assessed by the percentage change in B to a percentage change in A.