The Preparation of inputs constitutes pre purchasing activities and decides to a great extent the success of the purchasing system. The inputs to purchasing come in the form of requisition or indent from various departments and units of the organization. The success of purchasing department depends upon the quality of these inputs and also upon the ability of the purchasing department personnel to analyze the inputs to the fullest extent, the most important inputs are: purchase requisitions and their accompanying product specifications.
Purchase Requisitions or Purchase Indents
A purchase requisition is the primary and authorization document describing de needed items. Most organizations have standard requisition from for the use of all its departments. The format, however, ma\’ change from organization to organization. The three most common types of the requisition forms ate:
- Standard purchase requisition,
- Traveling purchase requisition, and
- Bills of materials
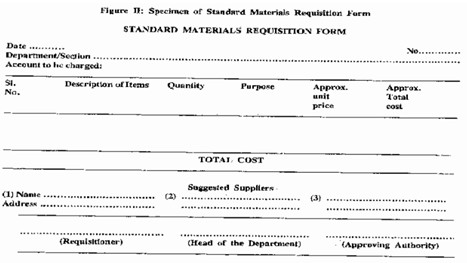
Standard Purchase Requisition Form: This form is standard for a given organization. Different organizations may use different formats. A standard purchase requisition form is used for non-recurring requirements of items and normally contains the following information:
- Requisition number (for identification, may use blocked codes including a short code for the department, name of the requisitioner, year, serial no. etc.).
- Date of the requisition.
- Name of the department/section
- Account to be charged (an appropriate head may be ticked out of standard account heads).
- Description and quantity of items
- Purpose of the items
- Date when items are needed
- Approximate unit price and the total cost.
- Suggested suppliers’ names and addresses
- Signatures of the requisitioner head of the department, approving authority (as appropriate).
A sample format of standard requisition form is shown in Figure II. Space may also be provided for the purchasing department to record:
- Purchase order no
- Shipping instructions
- Delivery date and quantity delivered.
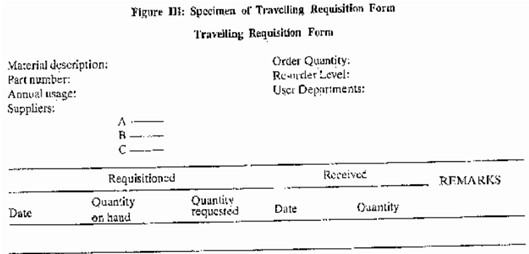
Traveling Purchase Requisition: This type of form is used by stores for recurring requirements for materials and standard parts. The requisition form is in the format of a card for a single item containing the information about the item (name and brief description, brief or coded names of the user department, annual usage rate, re-order point, and order quantity) potential suppliers, records of receipts and issues, and so forth. The card can be used for many requisitions. When the stock level drops to or below the re-order point, the card is sent to the purchasing department for placing the order with the supplier. Sometimes a separate requisition form which is a brief version of standard form, is also, used when it is not convenient to send the card to identify that the item is requisitioned, a colored signal clip is attached with the card until the order is received. The entire transaction can be handled with minimum delay and without much of clerical paper work.
A sample format of the traveling purchase requisition card is shown in Figure III.
Bill of Materials: This is a list of all items for a finished product and is prepared at the time of engineering drawing of the product. The bill of materials and the production schedule are sent to the purchasing department which computes the total requirements of each part for each period of the production. This eliminates the necessity of typing numerous requisitions for usually a large number of items.
Specifications
Specifications of an item intended to be purchased provide detailed description of the characteristics and features of the item. These must he provided by the requisitioning department by taking, if necessary, assistance from the purchasing department which has acquired specialization in the related matter. The major objectives of the specifications are: (1) to let the purchasing department understand exactly the features required in the item, (2) to let the supplier know exactly what the buyer wants, and (3) to permit the easier, quicker and accurate verification of items upon receipt. Following are the common types of specifications used to describe and grade the items:
Market Grade: Market grades are used in case of items bought and sold in a market place. Grading is done by comparison with a standard generally and widely accepted. Trade associations, commodity exchanges and government agencies establish and regulate such grades. Market grades are limited to natural products such as wheat, cotton, rice, lumber, etc. The suitability and success of this system, however, depend on the accuracy of grading and ability to ascertain the difference by inspection.
Commercial Standards: These standards are used for the items above commodity level because of their widespread use. When a material or item is standardized with complete quality description and established by customs, and accepted by the government, its agencies and industry in general, the material or item is said to be commercially standardized. Standard specifications have been prepared for many items by the Bureau of Indian Standards. Commercial standards have proved to be of great assistance in interchangeability for the user, and simplification of design, purchase procedure, inventory control, and cost reduction. These play vital role in mass production.
Trade or Brand Names: Trade or brand names are used by some manufacturers to establish the identity of various models produced and to protect them from other substitute. Branded products are simplest to buy, procedurally. Specifying an item by brand name limits the scope of competition and indicates reliance upon the integrity and reputation of the supplier to provide consistent quality. This system of specification can be very economical for low-cost lot purchases.
Material Specifications: These specifications define the physical or chemical properties desired in an item. Items such as metals (aluminum, steel, copper, etc.), drugs, oils and paints are examples of products with material specifications.
Performance Specifications: Rather than describing an item physically or chemically, performance specifications describe the requirements about the performance characteristics. The seller is free to choose the materials, methods of processing and other details. These specifications are commonly used in case of equipments, machines, tools etc. This method, however, requires proper selection of supplier. The items supplied are tested to see that stated performance features are met. Purchase of computer system is a good example of this technique.
Samples: In case of special items of non-repetitive nature or where quality requirement is not rigid or when the quantity of items is so low that it does not justify the formulation of specifications, specifications are established by specimens or samples. The supplier is supposed to match the sample. Difficulty arises if the samples are subject to change, physically or chemically. In case of mechanical parts for replacement where the identification marks are not easily read, this method of specifications by sample may be the only possible way of purchasing the item.
Blueprints: A blueprint or engineering drawing is recommended for accompanying a purchase requisition when close tolerance or a high degree of mechanical perfection is required. Blueprints are used for mechanical parts, and for construction and other projects.
Combined Specifications: Many products cannot be adequately described by a single type of specification. In such cases, a combination of two or more specifications may be used. Quite a few products for industrial uses are so complex that a combination becomes a practical necessity.

