An energy management system (EMS) is a system of computer-aided tools used by operators of electric utility grids to monitor, control, and optimize the performance of the generation and/or transmission system.
The computer technology is also referred to as SCADA/EMS or EMS/SCADA. In these respects, the terminology EMS then excludes the monitoring and control functions, but more specifically refers to the collective suite of power network applications and to the generation control and scheduling applications.
Manufacturers of EMS also commonly supply a corresponding dispatcher training simulator (DTS). This related technology makes use of components of SCADA and EMS as a training tool for control centre operators. It is also possible to acquire an independent DTS from a non-EMS source such as EPRI
Energy management systems are also often commonly used by individual commercial entities to monitor, measure, and control their electrical building loads. Energy management systems can be used to centrally control devices like HVAC units and lighting systems across multiple locations, such as retail, grocery and restaurant sites. Energy management systems can also provide metering, submetering, and monitoring functions that allow facility and building managers to gather data and insight that allows them to make more informed decisions about energy activities across their sites.
Any type of company responsible for the manufacturing of any type of product (hardware or software) consumes a large portion of total world energy. Energy management works under the following guideline:
- Plan – data acquisition, processing and documentation, energy target and objective, energy management and action plan
- Do – resources, raising awareness and training, communication, documentation, operation control
- Check – monitoring document, corrective and preventive action, planning and record, internal audit
- Act- management review
ISO 50001 is a new energy management systems standard. It concerns the discipline of energy management and, to avoid confusion with environmental management systems (EMS), energy management systems are abbreviated as EnMS. ISO 50001:2011 Energy management systems – Requirements with guidance for use is a specification created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for an energy management system.
In EMS, the main task was to manage the energy through various techniques like load management (LM), demand side management (DSM), distribution management systems (DMS). EMS are computer based programs that perform both computational tasks as well as decision making tasks so as to assist the operator for real time operation and control.
The evolution of SCADA started with monitoring and data acquisition systems plants followed by control. These have been used prior to EMS. The main tasks of SCADA were to continuously measure and monitor parameters for checking limit violations and to ensure reliable and safe operation of the system being controlled. The earlier tasks of SCADA were mostly monitoring with gradual control tasks coming into picture.
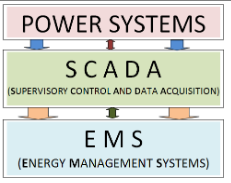
The figure below shows the main important entities of power systems, EMS and SCADA. EMS and SCADA are two important entities in the real time monitoring, operation control of power systems. The flow of Power and information between the three modules can be observed. While Power (unidirectional) flows from Power Systems through SCADA to EMS. Information flow (bi directional) SCADA forms the interface between Power Systems and EMS. The power system data, both continuous and discrete, is collected by SCADA and selectively sent to the EMS. EMS is a computerized control of power systems consisting of several application programs which are run / executed by the operator so as to maintain the power system in a secure and table operating state. EMS consists of several programs interconnected in a particular fashion so as to obtain the solution in real time.
EMS consists of a network of computers or work stations which perform computational tasks for decision making in real time operation and control. Both On-line and Off-Line functions can be performed in an EMS. The operators in an EMS send signals to the power system through SCADA. On line functions include mainly closed loop control functions like automatic generating control (AGC), load frequency control (LFC), voltage reactive power control (volt-var control). Open loop functions like Economic Dispatch and Operator load flow, state estimation, security assessment, etc are also performed in real time as on line functions.
The important working of an EMS is given below
- Real time monitoring and control over the whole distribution network.
- Enhanced customer service through a complete outage management package including trouble call taking, fault localization and restoration as well as outage statistics and customer notification.
- Efficient work order handling via the built-in work management tools.
- Better crew and resource management including support for crew scheduling and tracking, dispatching and assignments as well as follow-up and reports.
- Optimal network utilization using the State Estimator functionality for optimal feeder reconfiguration and loss minimization in balanced networks
Better support for all reporting with retrieval of historical data archived in a data warehouse

