Before we go through the mechanism of environmental analysis, it is desirable to understand the nature of environment, its impact on the organization, and various factors which constitute environment. An organization, being a system, operates in some contexts which lie outside it and is called as external environment or simply environment. Thus, environment consists of all the conditions, circumstances, and influences surrounding and affecting art organization in its totality or any of its subsystems. The environmental factors are quite broad. For example, Barnard has defined environment as follows:
“Environment consists of .atoms and molecules, agglomeration of things in motion, alive, of men and emotions, or forces and resistances. Their number is infinite and they are always present; they are always changing.
This is quite a broad description of the environment. In order to be more precise, an organization has to find out the relevant environment which directly affects it. However, the concept of relevance is a matter of perception which may differ from organization to organization and from strategist to strategist in the same organization. In order to define and identify the relevant environment, let us go through the exogenous nature of environment which has been presented in the figure.
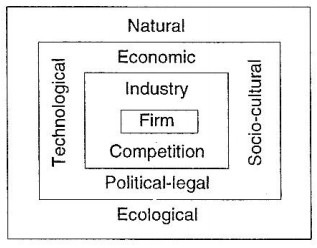
Figure: Exogenous nature of environment, the basic implication of the figure is that farther away an environmental variable exists from the firm, less impact it has over the firm’s operations.
Based on the nature of this impact, various environmental factors are grouped into two categories: general and specific.
General Environment: General Environment, also known as societal, remote, macro or indirect-action environment consists of those factors which affect the business of a country and, therefore, they have homogenizing effect. In the general environment, we can include natural and ecological factors at the first level. Natural factors are important to the economic activities of a country because’ either they provide opportunities or threats to the economic system.
At the second level, comparatively, more influential factors come in the form of economic, political-legal, technological, and social-cultural factors. Taken together, they set forth the framework for organizations’ operations and determine the inputs which organizations can take from the environment, process these inputs in the form of outputs, and export these outputs back to the environment. Various characteristics of such factors may be favorable or unfavorable to the growth of organizations. Besides these factors, which exist within a country, international factors also become important because of globalization of economy of a country.
Specific Environment: Specific environment, also known as task, operating, micro or direct-action environment, affects individual organizations differently. Since a particular organisation operates in an industry or limited number of industries, it is directly affected by the nature of industry concerned and the type of competition prevailing therein. Thus, the specific environment includes those forces lying outside the organisation directly relevant to decision making about input acquisition, transformation process, and export of output. However, it does not mean that an organisation should take the analysis of its specific environment only; it has to analyze general environment too because it ultimately shapes the specific environment.
Nature of Environment: Environment provides both, opportunities and threats. In order to know whether there is-an opportunity or threat, we have to look at the nature of environment in terms of its complexity and variability.

