Organization structure is the arrangement of people and tasks to accomplish organizational goals.
There are four basic types of sales organizational structure line, line and staff, functional, and committee.
The grouping of activities into positions and the charting of relationships of positions causes the organization to take on Structural form. The first two types (line and line and staff) are the most common. Functional and committee organizations are rare. Most sales departments have hybrid organizational structures, with variations to adjust for personalities and to fit specific operating conditions.
The sales department’s structure evolves from the needs of the business. No two companies have identical sales organizations, because no two have identical needs. The customers, the marketing channels, the company size, the product or product line, the practices of competitors, and the personalities and abilities of the personnel are but a few of the factors affecting the organizational structure of the sales department.
Lines Sales Organization
The line organization is the oldest and simplest sales organizational structure. It is widely used in smaller firms and in firms with small numbers of selling personnel-for instance, in companies that cover a limited geographic area or sell a narrow product line. The chain of command runs from the top sales executives down through subordinates. All executives exercise line authority, and each subordinate is responsible only to one person on the next higher level. Responsibility is definitely fixed, and those charged with it also make decisions and take action. Lines of authority run vertically through the structure and all persons on anyone organizational level is independent of all others on that level.
The line sales organization sees its greatest use in companies where all sales personnel report directly to the chief sales executive. In these companies this executive often is preoccupied with active supervision and seldom has much time to devote to planning or to work with other top executives.
Occasionally, however, the line sales organization is used where more than two levels of authority are present.
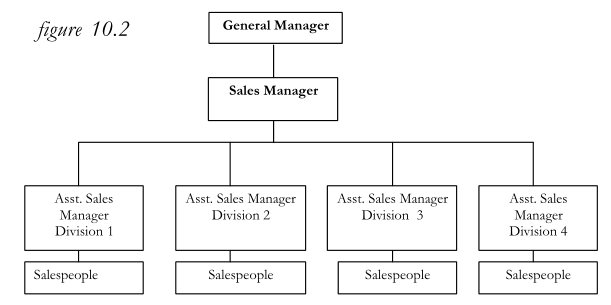
Figure 10.1 shows a fairly large sales department organized on the line basis. The sales manager reports to the general manager, assistant sales managers re-port to the sales manager, and salespeople report to assistant managers. Theoretically, there is no cross-communication between persons on the same level. Contacts between persons on the same level are indirect arid are effected through the next higher level. For example, the assistant sales manager of Division 1 arranges to confer with the assistant sales manager of Division 2 through the sales manager. Similarly, contacts by sales personnel with the office staff flow up through the organization to the sales manager and back down through the assistant sales manager in charge of the office to the office staff.
Advantages of Line Structure
- The basic simplicity of line organization is the main reason for its use.
- Be-cause each department member reports to only one superior, problems of discipline and control are small.
- Lines of authority and responsibility are clear and logical, and it is difficult for individuals to shift or evade responsibilities.
- Definite placement of authority and responsibility saves time in making policy changes, in deciding new plans, and in converting plans into action.
- The simplicity makes it easy for executives to develop close relations with salespersons. With this working atmosphere, it is not surprising that executives who come up through a line organization are frequently strong leaders. As the typical line sales department has few organizational levels, administrative expenses are low.
- Lines of authority and responsibility are clear and logical, and it is difficult for individuals to shift or evade responsibilities.
- Definite placement of authority and responsibility saves time in making policy changes, in deciding new plans, and in converting plans into action.
- The simplicity makes it easy for executives to develop close relations with salespersons. With this working atmosphere, it is not surprising that executives who come up through a line organization are frequently strong leaders. As the typical line sales department has few organizational levels, administrative expenses are low.
Weakness of the Line Sales Organization is that
- The head needs outstanding ability and rare qualifications, and should be well versed in all phases of sales management, for there are no subordinates with specialized skills and knowledge.
- Even if the head is an all-around expert, there is insufficient time for policymaking and planning, since rigidity of the line structure requires that a great deal of attention be given to direction of sales operations. The head often must make decisions and take action without benefit of planning. Under such conditions, results are often disappointing.
For rapidly growing concerns and for those with large sales staffs, the line organizational structure is inappropriate. As the department grows, new layers of executives must be added to retain control. Orders and directions must be passed down through a growing series of administrative levels. Moreover, as growth proceeds, earlier advantages of close relations among executives and salespeople are sacrificed and maintaining morale becomes a greater challenge.
Line and Staff Sales Organization
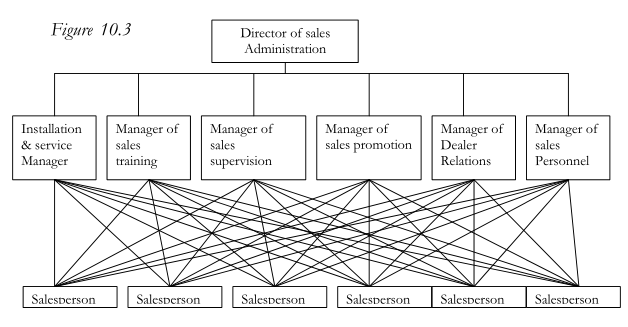
The line and staff sales department is often found in large and medium-sized firms, employing substantial numbers of sales personnel, and selling diversified product lines over wide geographic areas. In contrast to the line organization, the line and staff organization provides the top sales executive with a group of specialists-experts in dealer and distributor relations, sales analysis, sales organization, sales personnel, sales planning, sales promotion, sales training, ser-vice, traffic and warehousing, and similar fields. This staff helps to conserve the top sales executives’ time and frees them from excessively detailed work. They make it possible for their chiefs to concentrate their efforts where they have the most skill. If the top sales executive is not equipped, through prior training or experience, to handle certain problems, staff specialists assist in increasing over-all effectiveness of the department. Similarly, by delegating problems involving considerable study or detailed, analysis to staff executives the top sales executive has more time for planning and for dealing with higher-priority matters.
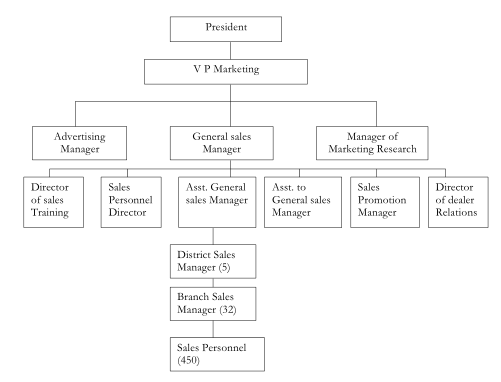
Staff sales executives do not have authority to issue orders or directives. Staff recommendations are submitted to the top sales executives, who if they approve, transmit necessary instructions to the line organization Figure 10.2 illustrates the line and staff sales organization. The general sales manager reports to the vice-president in charge of marketing as does the advertising manager and the manager of marketing research. Six subordinates report to the general sales manager, but only one, the assistant general sales manager, is a line executive. Four of the five staff executives have responsibilities in specialized fields; the fifth, the assistant to the general sales manager, is given more general assignments.
Note the difference between the assistant to and assistant. The assistant to is a staff executive who is given a broader operating area than those staff specialists with more descriptive titles. In contrast, the assistant has general line authority delegated by the superior. The assistant general sales manager is an understudy of the general sales manager who performs assignments of a line nature in the name of the superior. The assistant to the general sales manager carries part of the general administrative load that would otherwise be borne by the general sales manager.
The Advantages of the Line and Staff Organization
- The chief sales executive, being relieved from much detail work, can take a broader view of the department.
- Problems can be seen in clearer perspective, and connections between apparently unrelated problems are brought into focus.
- A pool of experts provides advice and assistance in specialized fields.
- Planning activities are subdivided and apportioned to staff members, and decisions and policies rests on a sounder base than lip the line organization.
- Meanwhile, the top sales executive can concentrate on control and coordination of subordinates. Staff members assume much of the burden of solving problems in their areas. Thus, the top sales executive can devote more attention to the human aspects of administration.
Weaknesses
- Work of the staff specialists must be coordinated, and this is costly. Other administrative expenses may also increase, unless the number of staff executives is kept in line with departmental needs. The staff should be expanded only when it can be shown that the contributions of new staff members will equal or exceed the costs of maintaining them.
- Close control over staff line relations is essential. If staff people issue instructions directly to line executives, it is difficult to prevent some persons from evading unwanted responsibilities
- When the line and staff sales organization is used, the time between problem recognition and corrective action tends to widen. This results from giving staff executives time to study problems before making recommendations to the decision makers.