Similar to prevalent and widespread maturity models as used in computing (CMM). Maturity Models is a classification which defines different levels of development in electronic delivery of governance.
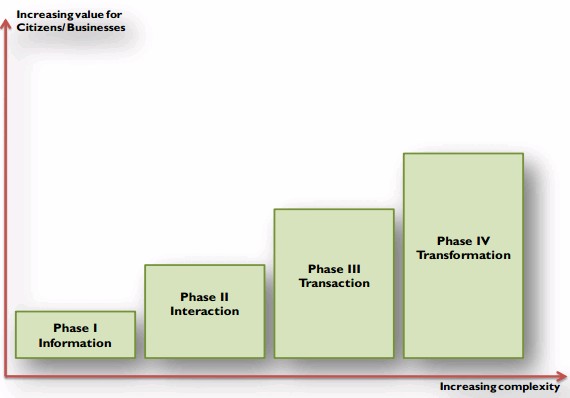
Most widely accepted maturity model is the “Gartner e-Governance Maturity Model”. The maturity model, comprises of ‘four’ phases, viz. Information, interaction, transaction and transformation. In each of the four phases, the delivery of online services and use of ICTs in government operations serve one or more of the aspects of e-Governance and the phases are
- Information: It means being present on the web, providing the external public (G2C and G2B) with relevant information. The value to the public is that government information is publicly accessible; processes are described and thus become more transparent, which improves democracy and service.
- Interaction: In the second phase the interaction between government and the public (G2C and G2B) is stimulated with various applications. People can ask questions via e-mail, use search engines for information and are able to download all sorts of forms and documents. These functionalities save time. In fact the complete intake of (simple) applications can be done online 24/7.
- Transaction: The complexity of the technology increases but, customer (G2C and G2B) value also increases. Complete transactions can be done without going to an office. Examples of online services are filing income tax, filing property tax, extending/renewal of licenses, visa and passports and online voting. Complexity is due to issues of security and personalization though it paperless transactions with legal certification. The complete process is online, including payments, digital signatures etc. This saves time, paper and money.
- Transformation: In it, all information systems are integrated and the public can get G2C and G2B services at one (virtual) counter. One single point of contact for all services is the ultimate goal. In this phase cost savings, efficiency and customer satisfaction are reaching highest possible levels.
- Connected Government – The UN e-Governance Survey 2008 report has taken this model a step further and introduced, as fifth phase, the concept of ‘Connected Government’, which means Governments transform themselves into a connected entity that responds to the needs of its citizens by developing an integrated back office infrastructure. This is characterized by
- Horizontal connections (among government agencies)
- Vertical connections (central and local government agencies)
- Infrastructure connections (interoperability issues)
- Connections between governments and citizens
- Connections among stakeholders (government, private sector, academic institutions, NGOs and civil society)