Six sigma
Six Sigma is a methodology that focuses on a quasi-perfect production process. Moreover, it refers to a methodology that aims at a rate of 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO).
Design Phase
- In the design phase of any process, there is identification and translation of the customers’ needs and expectations into Critical-To-Quality (CTQ) characteristics.
- Moreover, these characteristics are put into the products’ design so as to deliver it consistently and economically.
- After that, there is a measurement of process performance to know how the output against particular limits by the process capability.
Mathematical Six Sigma
- Six Sigma represents six standard deviations from the ‘mean.’ Moreover, this implies that if a company produces 1,000,000 parts/units, and its processes are at the Six Sigma level, less than 3.4 defects only will result.
- Moreover, the table below shows the number of defects observed for every 1,000,000 parts produced.
| Sigma Level | Defects per million opportunities |
| Two Sigma | 308,507 DPMO |
| Three Sigma | 66,807 DPMO |
| Four Sigma | 6,210 DPMO |
| Five Sigma | 233 DPMO |
| Six Sigma | 3.4 DPMO |
Few terms used in Six Sigma are,
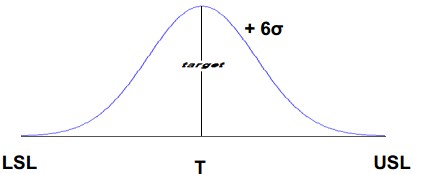
- Firstly, USL. It is the upper specification limit for a performance standard.
- Then, LSL – It is the lower specification limit for a performance standard.
- Lastly, Target – Ideally, this will be the middle point between USL and LSL.
Benefits of Six Sigma
- Firstly, continuous defect reduction in products and services.
- Enhancing customer satisfaction
- Then, process maintenance.
- After that, a sustainable competitive edge.
- Lastly, helpful in making the right decisions.
DMAIC Methodology
The Six Sigma methodology is conceptually based on a five-phase project. Moreover, each phase has a specific purpose and specific tools and techniques.
All the five phases are,
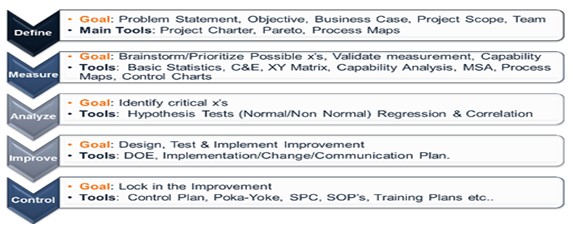
Define Phase:
Most importantly, the goal of Define is to establish the project’s foundation and is the most important aspect of the Six Sigma project. After that, there is the completion of the specification of problems and goals the remaining tasks of valuation, team, scope, project planning, timeline, stakeholders, VOC/ VOB, etc. Moreover, various tools used by the Define Phase are
- Project Charter
- Problem Statement
- Business Case
- Objective
- High-level timeline, etc.
Measure Phase:
In this phase, there is a collection of baseline information about the process or product and achieve the following objectives,
- Firstly, gather All possible x’s.
- Analyze measurement system and Data Collection Requirements.
- After that, Validate Assumptions and Improvement Goals.
- Determine COPQ.etc.
This Phase involves the usage of the following tool,
- Process Maps, Value Stream Mapping
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- Cause and Effect Diagram
- XY Matrix
- Basic Control Charts
- Six Sigma Statistics
- Basic Statistics.etc.
Analyze Phase:
Firstly, this phase requires establishing verified drivers by using statistics and higher-order analytics to discover the fact on the basis of the relationship between the process performance and the root causes.
Moreover, this phase establishes transfer function Y=f(x) and validates the list of critical X’s and their impacts. And, this phase utilizes various tools like,
- Hypothesis Testing
- Simple Linear Regression
- Multiple Regression
Improve Phase:
This phase is for making the improvement like improving the designing, testing and implementing of the solution. Moreover, it involves enlisting statistically proven results from active study or pilot, creating the improvement plan, updating the stakeholder assessment, and adding new process capability.
This phase uses tools like
- Firstly, the design of Experiment (DOE).
- Implementation Plan.
- Then, Change Plan.
- Communication Plan.
Control Phase:
It is the last phase of the methodology that establishes automation mechanisms to maintain and sustain improvements in the process. Moreover, a successful control plan also results in a reaction and mitigation plan with an accountability structure. Above all, the Six Sigma methodology is a complete system with tools and techniques built-in to achieve success.
Excellence Model
- Excellence approaches such as the EFQM Excellence Model and six sigma are complementary vehicles for achieving better organizational performance.
- Moreover, the Excellence Model plays a key role in the baselining phase of strategic improvement. On the other hand, the six-sigma breakthrough strategy is a delivery vehicle for achieving excellence through:
- Committed leadership.
- Integration with top-level strategy.
- A cadre of change agents – Black Belts.
- Customer and Market focus.
- Bottom-line impact.etc.
Learn and enhance your skills in Six sigma. Become a Certified TQM Professional Now!

