What is Quality Function Deployment (QFD)?
We can define Quality Function Deployment as a method for prioritizing and translating customer inputs into designs and specifications for a product, service, and/or process. Moreover, the essentials of the QFD method derives from common-sense ideas and tools. Above all, QFD is a planning tool that relates a list of delights, wants, and needs of customers to design technical functional requirements. Moreover, the voice of the customer can be discounted into a list of needs to use it later as input to a relationship diagram, which is known as QFD’s house of quality. In the context of DFSS, these requirements critical-to characteristics, which include subsets such as critical-to-quality (CTQ) and critical-to-delivery (CTD).
Quality Function Developement Advantages
- Firstly, QFD is the attainment of shortest development cycle mostly gained by the companies with the ability to satisfy customer expectation.
- Secondly, it is gain of improvement in the design family of the company, results in increasing customer satisfaction.
- Lastly, in the QFD methodology, customers define the product using their own expressions, which rarely carry any significant technical terminology.
QFD Application Variations
- Firstly, prioritizing and selecting improvement projects on the basis of customer needs and current performance.
- Assessing a process’s or product’s performance versus competitors.
- Then, translating customer requirements into performance measures.
- Lastly, designing, testing and refining new processes, products, and services.
QFD Methods
- Voice of the Customer input to Design of Experiments, to work well.
- A special multidimensional matrix, also known as the “House of Quality,” is the best-known element of the QFD method.
QFD Concepts
QFD concept involves two core concepts, which are
-
The QFD Cycle
This is the first concept of QFD. In this a frequent efforts for developing operational designs and plans in four phases of,
- Translating customer input and competitor analysis into product or service features.
- Then, translatingoduct/service features into product/service specifications and measures.
- Translating product/service specifications and measures into process design features.
- Translating process design features into process performance specifications and measures.
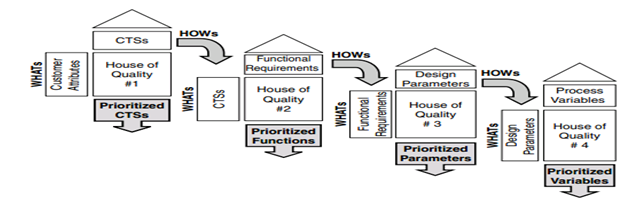
Accomplishment of QFD is by multidisciplinary DFSS teams using a series of charts to deploy critical customer attributes throughout the phases of design development.
Deployment of Quality Function Deployment is usually done over four phases. The four phases are,
- Firstly, CTS planning
- Second phase, unctional requirements
- Then, design parameters planning
- Lastly, process variables planning, as shown in the figure below.
-
Prioritization and Correlation
This is the second concept of QFD. In this there is analysis of the relationships among specific needs, features, requirements, and measures in detail.
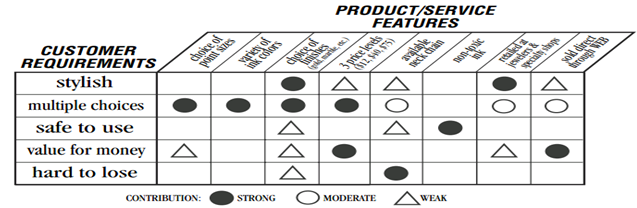
House of Quality
Matrices like the House of Quality or the simple L-Matrix keep this analysis in a well manner. And document the rationale behind the design effort.
Above all, House of Quality is a “diagonal” relationship test that matrix affords. And it do not considers testing combinations by our standard human “linear” thought processes. An example is shown below
QFD analysis
This is includes six steps which are,
- Firstly, it starts with the articulation of customer requirements. It uses techniques that are interviewing, observation, prototyping, conceptual modeling, etc. It also uses data from marketing research.
- Secondly, the rank of company’s current product is against the competitors.
- Next, the team looks at Product/Process Characteristics, in other words, the “How’s” of meeting the customer requirements. In this they consider and rank the candidate CCR’s which are on the top and for as to which will address customer needs.
- Then, the team relates customer and technical requirements with ratings such as “high”, “moderate”, “low”, and “no” correlation.
- In the fifth step, the roof of the “House” focuses on relationships among product/process characteristics. It shows whether the “How’s” reinforce or conflict with one another.
- In last, the team summarizes the key conclusions. It ranks the relevance of product or process characteristics to the attainment of customers’ wants or needs.
Enhance and Upgrade your design process skills for better career opportunities. Become a Certified TQM Professional Now!